In this modern world, data is in available in every field. Data from social media interactions, online purchases and sensor data from smart devices, we are generating massive amounts of data every hour. Utilizing this data can lead to innovative information that push innovation further and provide a competitive edge for businesses. But people generally ask: what is big data? What is data analytics? and what is data science?
In this guide, we shall discuss these terms and compare them as big data vs data analytics vs data science. also we shall discuss the challenges and opportunities associated with big data and explore how data analytics is applied across various industries.
What is Big Data?
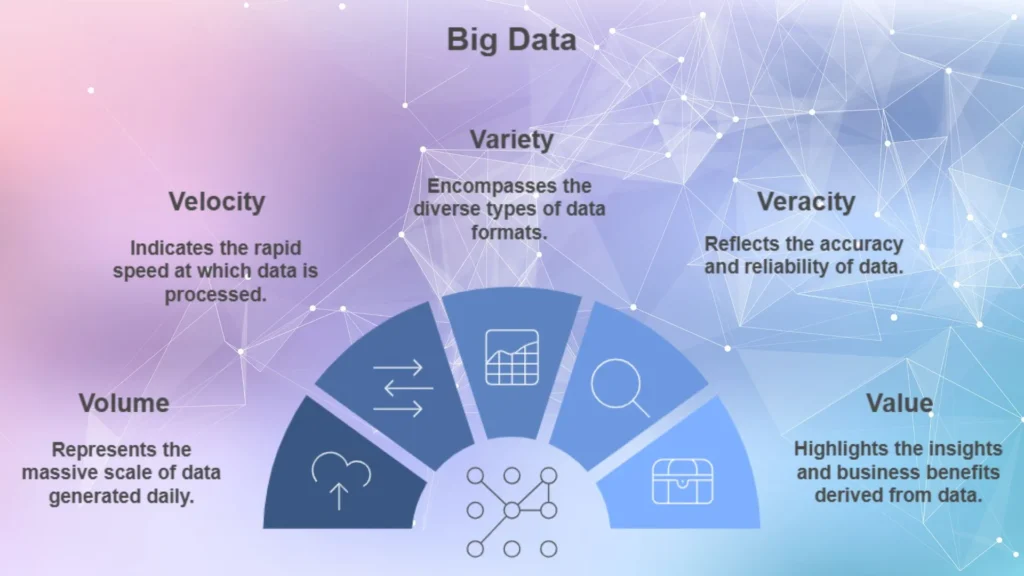
Big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that traditional data processing software cannot handle effectively. Big data is characterized by the five Vs:
1. Volume: The sheer amount of data generated every day, from terabytes to petabytes.
2. Velocity: The speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed.
3. Variety: The different types of data, including structured data (like databases) and unstructured data (such as images, videos and social media posts).
4. Veracity: The reliability or accuracy of the data, which can vary based on its source.
5. Value: The potential information and business value that can be derived from analyzed data.
Example of Big Data in Action
Consider a company like Amazon, which collects massive amounts of data on customer behavior, product searches, purchasing patterns and feedback. This data helps Amazon to improve customer experience by suggesting relevant products, optimizing logistics and enhancing customer service.
What is Data Analytics?
Data analytics is the process of examining datasets to discover trends, patterns and information. Although big data focuses on the large data, data analytics focuses on making sense of this data. Data analytics is generally broken down into four main types:
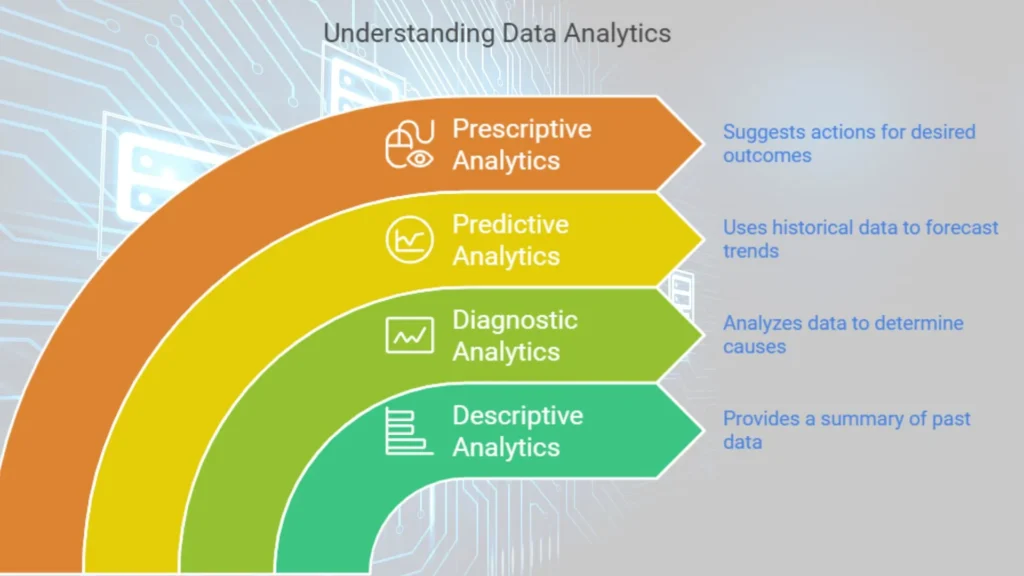
1. Descriptive Analytics:
Provides a summary of past data (e.g., sales reports).
2. Diagnostic Analytics:
Analyzes data to determine why something happened (e.g., why sales dropped in a specific quarter).
3. Predictive Analytics:
Uses historical data to predict future trends (e.g., forecasting next month’s sales).
4. Prescriptive Analytics:
Suggests actions to achieve a desired result (e.g., recommending marketing strategies to increase sales).
Real World Example of Data Analytics
Netflix is a great example of a company using data analytics. By analyzing user behavior, Netflix provides personalized recommendations to viewers. This enhances user experience and also helps Netflix retain subscribers.
What is Data Science?
Data science is similar field that uses scientific methods, algorithms and systems to extract information from structured and unstructured data. It combines elements of statistics, computer science and domain expertise to analyze data, build models and predict future results.
Data science goes beyond traditional data analytics. It creates predictive models and uses machine learning to make decisions. Although data analytics is generally focused on interpreting existing data, data science is about generating new information and creating intelligent systems.
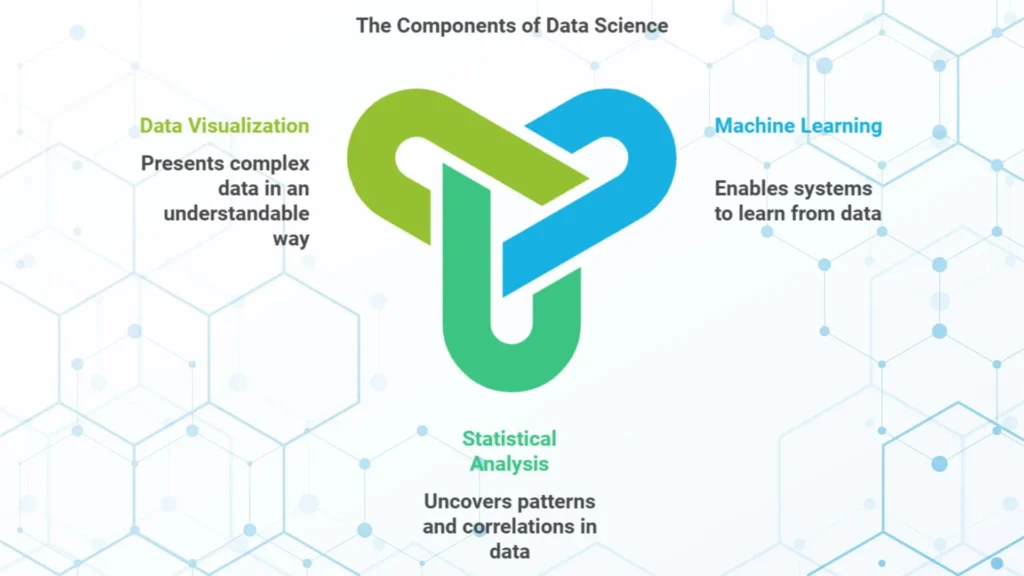
Key Tools and Techniques in Data Science
– Machine Learning: A branch of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without special programming.
– Statistical Analysis: It collects and analyzes data to discover patterns and correlations.
– Data Visualization: Tools like Tableau and Power BI help data scientists to present complex data in a format that is easy to understand.
Real World Example of Data Science
Uber uses data science to optimize its ride sharing platform. By analyzing data on traffic patterns, demand for rides and driver availability. This helps Uber to reduce waiting times and improve its pricing models.
Key Challenges and Opportunities with Big Data
While big data holds tremendous potential, it also presents significant challenges. Here is a closer look at the main challenges and how they can be turned into opportunities:
1. Data Privacy and Security
– Challenge: With more data collected, there is a higher risk of data breaches and privacy violations.
– Opportunity: Improved data encryption, stricter access controls and regulatory compliance (like GDPR) can protect sensitive information and build consumer trust.
2. Data Quality and Accuracy
– Challenge: The accuracy of information depends on the quality of data, which may contain errors, duplications or inconsistencies.
– Opportunity: Investing in data cleansing and validation processes can enhance the reliability of data analytics and decision making.
3. Scalability and Storage
– Challenge: As data volumes grow, organizations struggle to store and process data efficiently.
– Opportunity: Cloud based solutions and scalable data storage architectures like Hadoop and Spark to enable companies to handle massive datasets with ease.
4. Talent Shortage
– Challenge: There is a high demand for skilled data scientists and analysts, but the talent pool is limited.
– Opportunity: Upskilling existing employees and investing in data science education can bridge this gap, which allows businesses to make the most of their data.
Applications of Big Data Analytics Across Industries
Big data analytics is transforming industries around the world. Here are some of the most impressive applications:
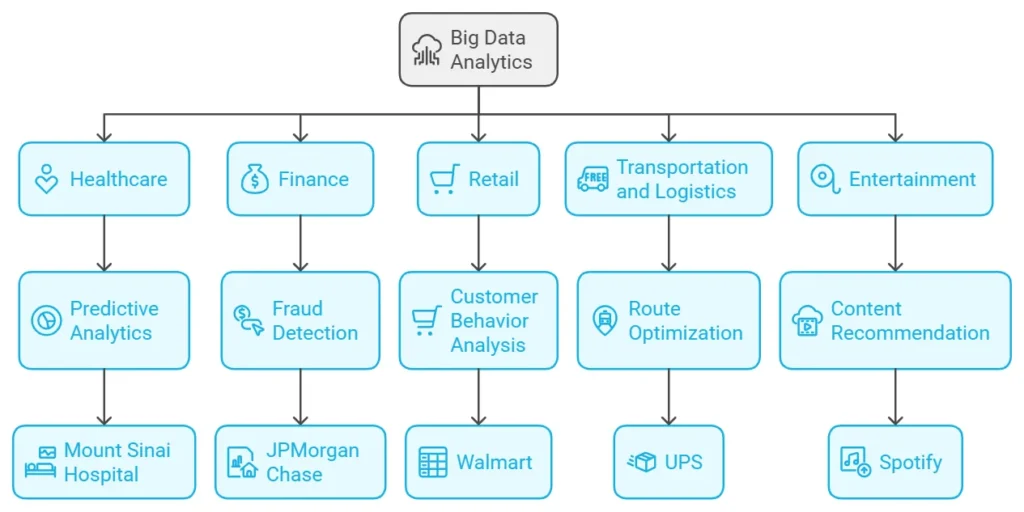
1. Healthcare
– Use Case: Predictive analytics helps hospitals to forecast patient admissions and manage resources effectively.
– Example: Mount Sinai Hospital uses big data to predict which patients are at risk of developing chronic conditions, which enables them to make early intervention.
2. Finance
– Use Case: Banks and financial institutions use big data to detect fraudulent transactions and assess credit risk.
– Example: JPMorgan Chase leverages big data analytics to identify potentially fraudulent transactions in real time, which protects customers and reduces financial losses.
3. Retail
– Use Case: Retailers analyze customer behavior to optimize inventory, personalize marketing and improve customer experience.
– Example: Walmart uses big data to manage its vast inventory, predict demand and keep its shelves stocked with the products customers want.
4. Transportation and Logistics
– Use Case: Companies use big data analytics to optimize delivery routes and reduce fuel consumption.
– Example: UPS uses a data driven route optimization system called ORION, which saves millions of miles each year and significantly reduces fuel costs.
5. Entertainment
– Use Case: Streaming services analyze viewer data to recommend content and keep subscribers engaged.
– Example: Spotify uses big data to personalize playlists based on user listening habits, which enhances user experience and retention.
The future of Big Data, Data Analytics and Data Science
As technology progresses, so do the capabilities and applications of big data, data analytics and data science also progresses. Here are some future trends of this field:
– Increased Adoption of AI and Machine Learning: Machine learning will continue to automate data analysis, which makes predictions more accurate and efficient.
– Edge Computing: With the rise of IoT, edge computing enables data to be processed closer to its source, which reduces latency and enables real-time analytics.
– Greater Focus on Data Privacy: As data collection grows, regulatory bodies will impose stricter standards to protect consumers, which makes data privacy a priority for businesses.
Key Takeaways
1. Big Data is vast and complex, characterized by the five Vs: Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity and Value.
2. Data Analytics interprets data to provide information, which consists of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive analytics.
3. Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that builds predictive models and uses algorithms to extract information, with tools like machine learning and statistical analysis.
Conclusion
Together, big data, data analytics and data science are pushing innovation further and helping businesses to make decisions based on analyzed data across industries.
By understanding and using these fields, organizations can gain a competitive advantage and discover the full potential of their data to create value, push growth further and stay ahead in the competitive global market.

