Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks and data from digital attacks. These attacks aim to steal or alter sensitive information, damage hardware or software, cause service disruptions or extort money. Now a days, these attacks can be simple data theft or a sophisticated, large scale data breaches that can disrupt organizational operations. A cyberattack can have devastating effects like financial loss, reputational damage and disrupted operations.
Cybersecurity is also known as internet security. In this article we shall discuss what is cybersecurity and various types of threats and the best practices to avoid them and stay protected.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Rising Threats: More people, devices and apps mean a greater need for cybersecurity. Cyber attackers are becoming more skilled and varieties in their methods.
Data Protection: Businesses handle a large amount of sensitive data. Protecting this data is very important to maintain trust and operational integrity.
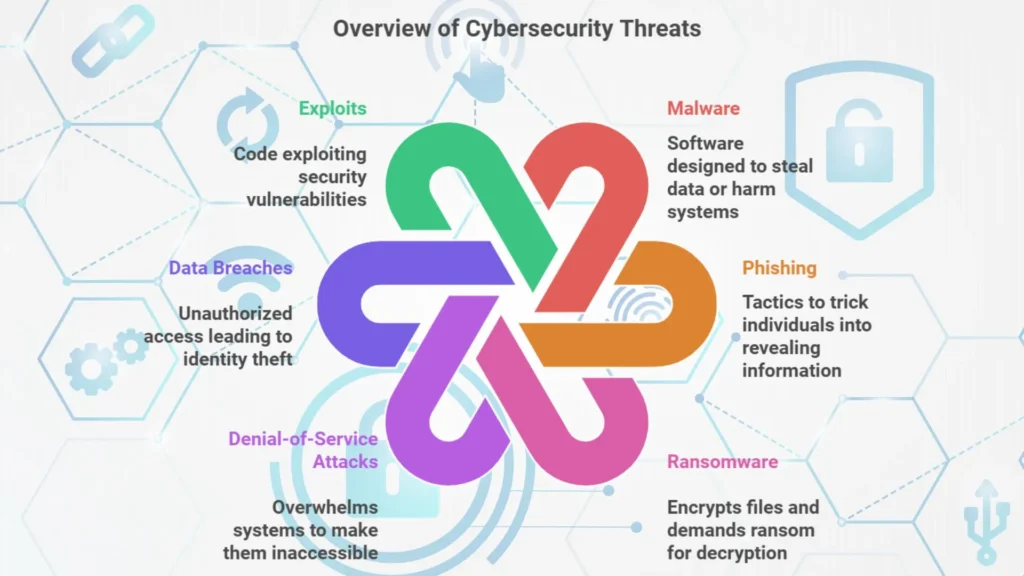
Some of the most common threats include:
1. Malware:
Malware means Malicious Software designed to steal data or harm computer systems, such as viruses, worms and ransomware. Many threats come from within, generally due to employee errors or rogue actions.
2. Phishing:
Phishing means deceitful tactics used by hackers to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, through fraudulent emails or messages. Modern phishing emails look very legitimate and can easily trick employees.
3. Ransomware:
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files and demands a ransom for decryption.
4. Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks:
Overwhelming a computer system or network with traffic to such a level that it becomes inaccessible to the user.
5. Data Breaches:
Unauthorized access to sensitive data, which results in identity theft or financial fraud.
6. Exploitation:
Code that takes advantage of security vulnerabilities. Password cracking software can break complex passwords. Use two factor authentication.
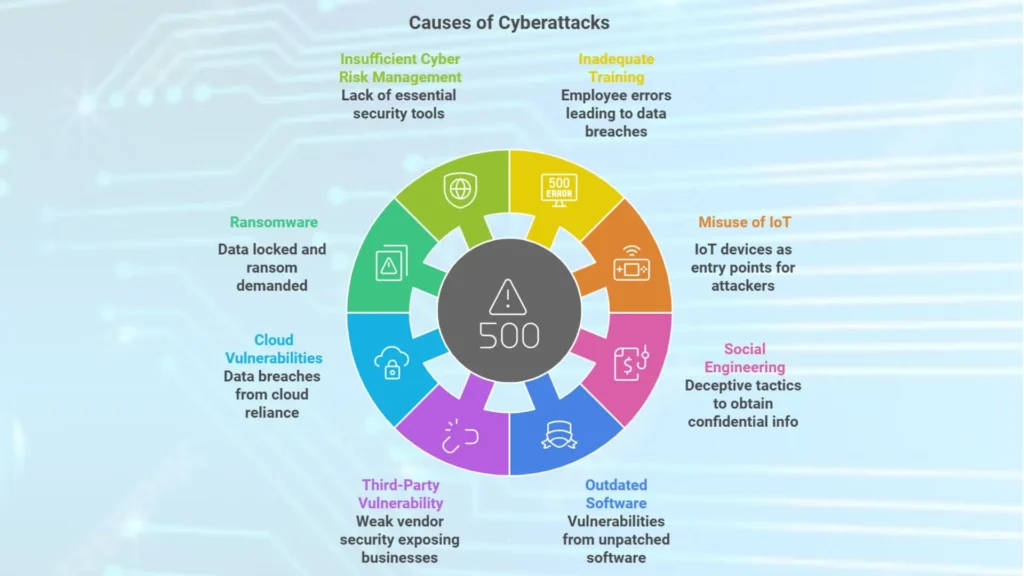
Common causes of Cyberattacks:
1. Inadequate Training for Employees: Employee errors account for 88% of data breaches.
2. Misuse of IoT: IoT devices are convenient but also provide entry points for cyber attackers.
3. Social Engineering: Attacks that deceive individuals into giving away confidential information.
4. Outdated Software: Creates vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
5. Third-Party Vulnerability: Vendors may have weak security, exposing your business to risks.
6. Cloud Vulnerabilities: Increased reliance on the cloud can lead to data breaches.
7. Ransomware: Locks data and demands ransom, which causes financial and operational damage.
8. Insufficient Cyber Risk Management: Lack of tools like two factor authentication and endpoint security.
9. Misinterpreting Compliance for Security: Compliance doesn’t guarantee security.
10. Outdated Hardware: Lacks the latest security patches, which makes it vulnerable to cyberattacks.
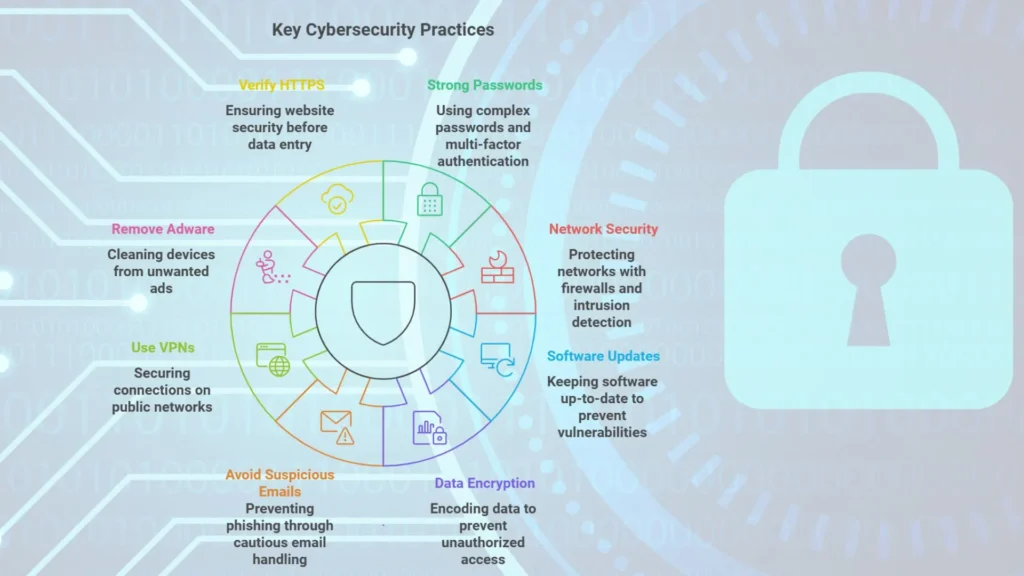
Key Cybersecurity Practices
To reduce these threats, organizations and individuals should adopt a systematic approach to cybersecurity:
1. Strong Password Practice: Use complex, unique passwords for each account and enable multi factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible.
2. Network Security: Employ firewalls, intrusion detection systems and other security measures to protect network infrastructure.
3. Regular Software Updates: Keep operating systems, applications and security software up-to-date to prevent vulnerabilities.
4. Data Encryption: Encode data to prevent unauthorized access. Use Secure File Sharing Software, Encrypt data during transfers.
5. Avoid Suspicious Emails: Do not open or click on links from unknown sources. Check Links Before Clicking, ensure links are legitimate.
6. Use VPNs: Protect your connections, especially on public networks.
7. Remove Adware: Clean your devices from unwanted ads.
8. Verify HTTPS: Ensure websites are secure before entering data. Use HTTPS on Your Website, secure your site to protect visitors.
9. Avoid Storing Information in Non-Secure Places: Use secure storage solutions.
10. Scan External Devices: Check for viruses before connecting to your network.
11. Avoid Public Networks: Use secure connections whenever possible.
12. Comply with Industry Regulations: Follow standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and GDPR.
13. Hire Penetration Testing Companies: Use white hat hackers to test your security.
14. Data Backup and Recovery: Implement robust backup and recovery plans to protect critical data from loss or corruption.
15. User Awareness and Training: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices. They should know how to recognize phishing attempts and how to avoid suspicious links.
16. Incident Response Planning: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to effectively respond to cyberattacks.
Common Cybersecurity Terms:
– Authentication: Verifying the identity of a user.
– Encryption: Encoding plaintext into ciphertext.
– Firewall: Network security system designed to block unauthorized access.
– VPN (Virtual Private Network): Encrypts a secure, private network from a public internet connection.
– Cloud: Software and services accessed over the internet rather than locally.
– Antivirus: A software to detect malware in computer system. A good cybersecurity strategy includes multiple layers, not just antivirus software.
The Role of Cybersecurity Professionals
Cybersecurity professionals play a important role in safeguarding digital assets. They work to identify vulnerabilities, implement security measures and respond to cyberattacks. As the number of threats increase day by day, the demand for skilled cybersecurity experts continues to grow.
Conclusion
The future of cybersecurity is marked by increasing complexity and sophistication. As technology advances, the tactics used by cybercriminals also advances. To stay ahead of these threats, organizations must invest in top and newest security solutions and continuously adapt their strategies.
Understand the importance of cybersecurity and implement best security practices. This way individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and protect their valuable digital assets.


I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.