You must have heard the term ‘malware’ in conversations about cybersecurity, but what exactly it is? More importantly, how does it affect your computer?
In this guide, we shall discuss about various types of malware and how to prevent them. We shall study their impact on your computer and explain how each one can compromise your system’s performance and security.
What Is Malware?
Malware, short form for malicious software, is any software designed to harm, exploit or otherwise compromise a computer system. It comes in many forms, each designed to damage devices, steal data or cause operational issues. It can display attractive ads and then lock you out of your own system, thus malware can make havoc in many ways.
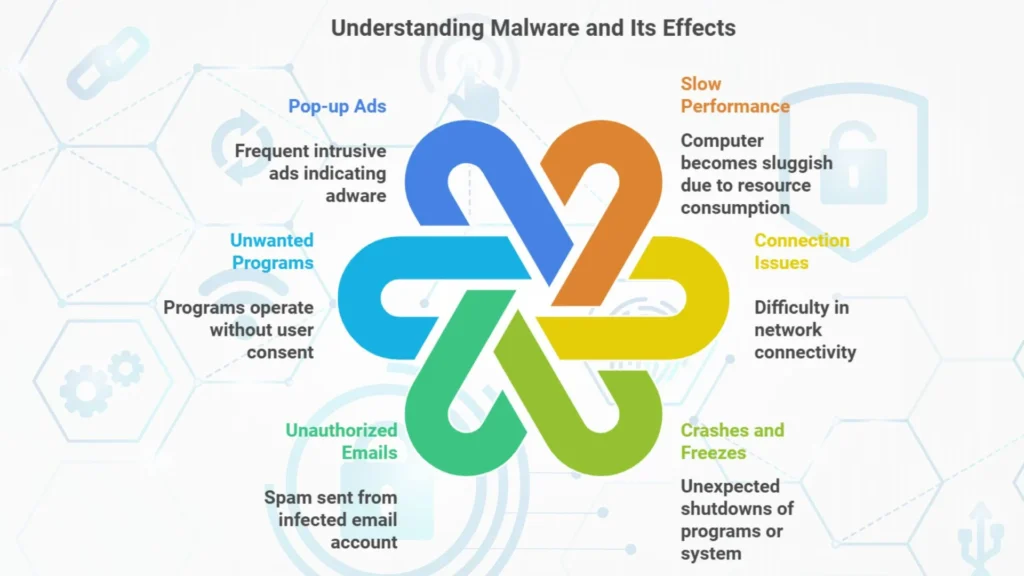
Here are some common signs that your computer may be infected by malware:
– Slow performance: Your computer may become sluggish as malware consumes resources.
– Connection issues: Difficulty connecting to networks could indicate a malware infection.
– Crashes and freezes: Programs or your entire system may shut down unexpectedly.
– Unauthorized emails: Malware can use your email account to send spam without your knowledge.
– Unwanted programs: If programs are running or shutting down on their own, malware may be involved.
– Pop-up ads: These ads, especially frequent and attractive ones, can be a sign of adware infection.
If you are experiencing any of these issues, don’t worry. Most malware can be removed with the help of professionals.
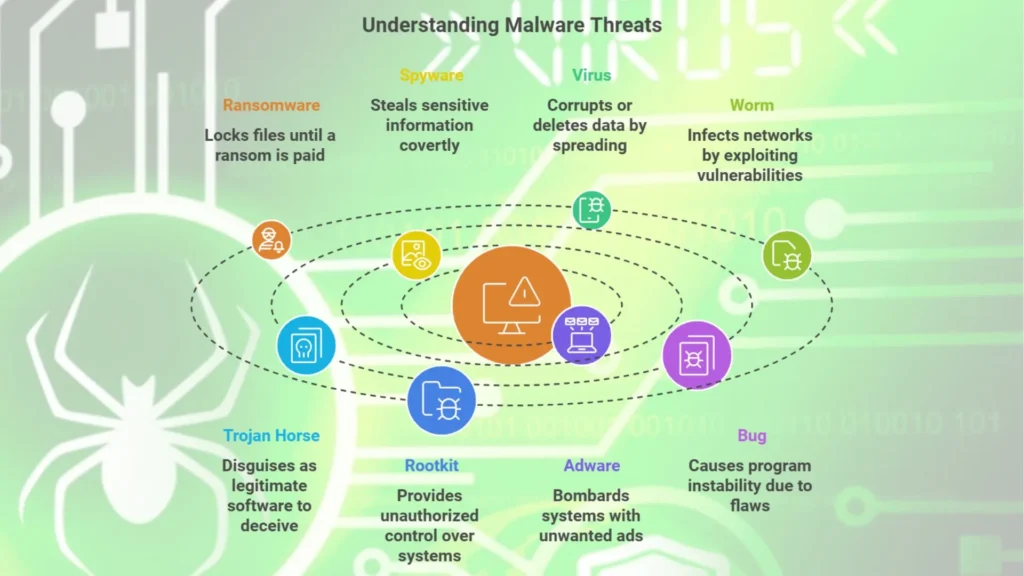
Different Types of Malwares and Their Effects
Let us explore the different types of malwares and how they impact your system:
1. Ransomware
– Impact: Ransomware locks you out of your computer or files until you pay a ransom. Recent outbreaks like WannaCry, Bad Rabbit, and NotPetya have shown just how devastating ransomware can be for businesses and individuals.
– How It Works: Ransomware encrypts your data, which makes it inaccessible. Hackers then demand a ransom in exchange for a decryption key.
2. Spyware
– Impact: Spyware un-knowingly tracks your activities. Then it steals sensitive information like passwords, browsing habits and financial details.
– How It Works: Spyware operates in the background. They collect data without your knowledge and transmits it to hackers.
3. Virus
– Impact: A virus attaches itself to legitimate files and spreads throughout your system. Thereafter it corrupts or deletes data.
– How It Works: Like a biological virus, it replicates itself. Then it infects more files and spreads to other systems through networks or removable drives.
4. Worm
– Impact: Worms can infect entire networks by exploiting vulnerabilities in network interfaces. Once inside, they spread to connected devices.
– How It Works: Unlike viruses, worms don’t need a host file. They self replicate and move through networks, which often causes widespread damage.
5. Trojan Horse
– Impact: A Trojan horse disguises itself as legitimate software to trick users into downloading it. Once installed, it can create backdoors for hackers to access your system.
– How It Works: Trojans generally looks as useful programs or files but they install malware once downloaded.
6. Rootkit
– Impact: Rootkits are among the most dangerous types of malwares. They provide unauthorized users with control over your computer, which allows them to steal information or manipulate software.
– How It Works: Rootkits can hide their presence by embedding themselves deep in the system, which makes them difficult to detect and remove.
7. Adware
– Impact: Adware, or advertising supported software, floods your system with unwanted ads, such as pop up banners.
– How It Works: Adware generates revenue for its creators by bombarding you with ads. While not always harmful, adware can slow your computer and be incredibly annoying.
8. Bug
– Impact: Bugs are flaws in a program’s source code that can affect performance or even cause system crashes.
– How It Works: While not as intentionally harmful as other malware, bugs can disrupt your productivity by making programs unstable or unusable.
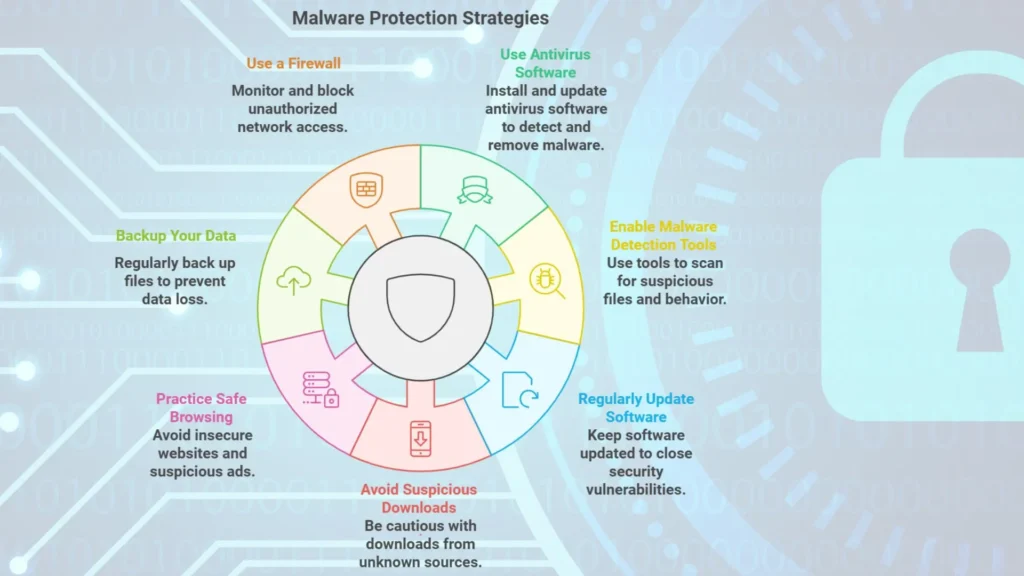
How to Protect Against Malware
All forms of malware can seriously disrupt your system, compromise your data and decrease productivity. To Protect your devices from these threats is very important. Here are some practical steps you can take:
1. Use Antivirus Software
Install reputable antivirus software that can scan, detect and remove malicious software. Ensure it is always updated with the latest virus definitions.
2. Enable Malware Detection Tools
Malware detection tools provide an additional layer of protection by scanning for suspicious files and software behavior.
3. Regularly Update Software
Outdated software can contain security vulnerabilities that malware can exploit. Keep your operating system and applications updated to reduce this risk.
4. Avoid Suspicious Downloads
Be cautious when downloading files, especially from unknown sources. Always double check the legitimacy of a file before downloading it. This will save you from becoming a victim of malware like Trojans or ransomware.
5. Practice Safe Browsing
Don’t click on suspicious ads or visit insecure websites. Use a browser with built in security features and also install extensions to block ads and trackers.
6. Backup Your Data
Regularly back up your important files to prevent permanent data loss in case of a malware attack, especially ransomware.
7. Use a Firewall
A firewall monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic. which then identifies and blocks malicious connections and unauthorized access to your system.
Conclusion
If you suspect your computer is infected with malware, it is important to act quickly to prevent further damage. Take professional expert help to detect, remove and prevent future malware infections.
By staying alert and using the right tools, you can protect your computer from many types of malwares available on the internet.