Now a days, we hear about ‘data encryption’. But what is data encryption? how does data encryption work? and how does data encryption ensure data privacy?
In this digital world, the data is a very important asset. To protect it from unauthorized access is very important. Data encryption is one of the most effective ways to safeguard sensitive information.
This guide explains it in simple terms, covering the basics, real-world applications and how does data encryption ensure your data to remain safe and private.
What Is Data Encryption?
Data encryption is the process of converting information into a coded format that can only be read by authorized parties. This process transforms plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (unreadable data). To decrypt the data and convert it back into its original form, the recipient needs a decryption key.
Encryption serves as a protective layer that prevents unauthorized users from accessing sensitive information, whether it’s in storage or being transmitted over a network. It’s widely used in various sectors, including finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and personal communications.
By ensuring that only those with the correct decryption keys can access the original information, encryption plays a key role in maintaining confidentiality and trust in digital systems.
How Does Data Encryption Work?
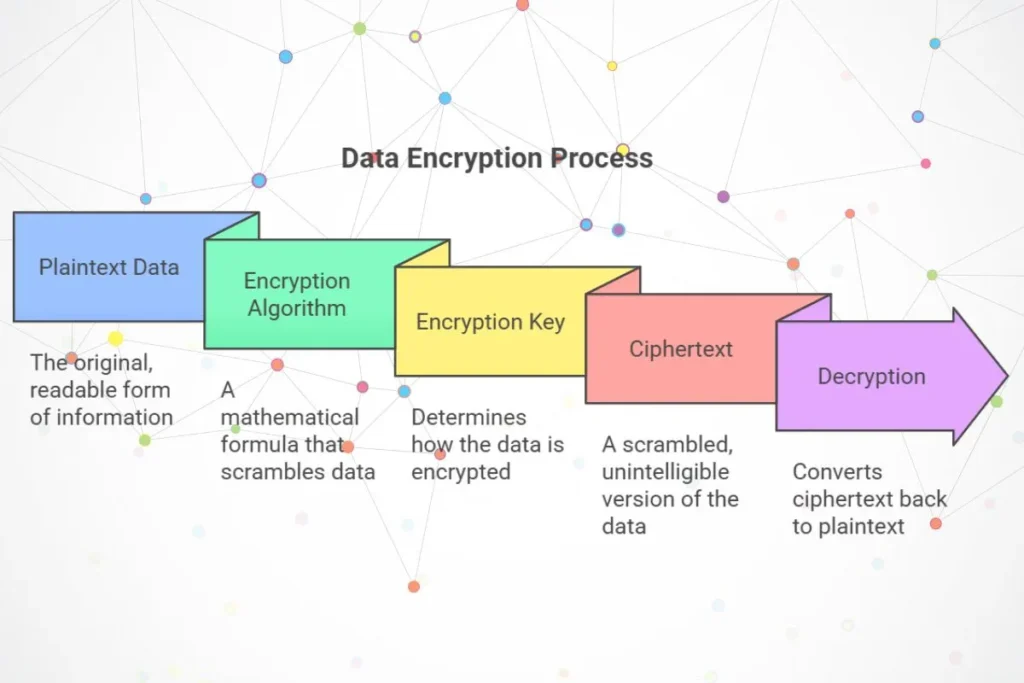
Data encryption relies on algorithms and keys to encode and decode information. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Plaintext Data
- The process begins with plaintext data, which is the original, readable form of the information.
- Encryption Algorithm
- The plaintext is passed through an encryption algorithm, a mathematical formula designed to scramble the data.
- Encryption Key
- An encryption key is applied to the algorithm. This key determines how the data will be encrypted. Without the key, the encrypted data remains unreadable.
- Ciphertext
- The output is ciphertext, a scrambled version of the original data. It looks like a random string of characters and is unintelligible without the decryption key.
- Decryption
- To convert the ciphertext back to plaintext, the recipient uses a decryption key and applies it to the algorithm in reverse.
This straightforward process underpins the security of most modern digital systems, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected.
Types of Encryption
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric.
1. Symmetric Encryption
- How It Works: The same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
- Use Cases: Suitable for encrypting large amounts of data, such as files and databases.
- Example: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
- Strengths: Faster than asymmetric encryption.
- Weakness: Key distribution can be a security risk since both parties must have the same key.
2. Asymmetric Encryption
- How It Works: Uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- Use Cases: Ideal for secure communications, such as email encryption and digital signatures.
- Example: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
- Strengths: Eliminates the need to share the private key.
- Weakness: Slower than symmetric encryption and not suitable for encrypting large data sets.
By using these encryption types effectively, organizations can build comprehensive security strategies tailored to their needs.
Real-World Examples of Data Encryption
- Online Banking
- Encryption protects sensitive information like account numbers and passwords during online banking transactions. Without encryption, this data could easily be intercepted by malicious actors.
- E-Commerce
- Websites use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols to encrypt payment details during online purchases, ensuring customer data remains confidential.
- Messaging Apps
- Apps like WhatsApp and Signal use end-to-end encryption to secure conversations. This ensures only the sender and receiver can read the messages, preventing eavesdropping even by the service providers.
- Cloud Storage
- Services like Google Drive and Dropbox use encryption to protect data stored in the cloud. This ensures that even if a breach occurs, the data remains unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Healthcare Systems
- Encryption protects sensitive patient records, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA while safeguarding patient confidentiality.
How Does Encryption Ensure Data Privacy?
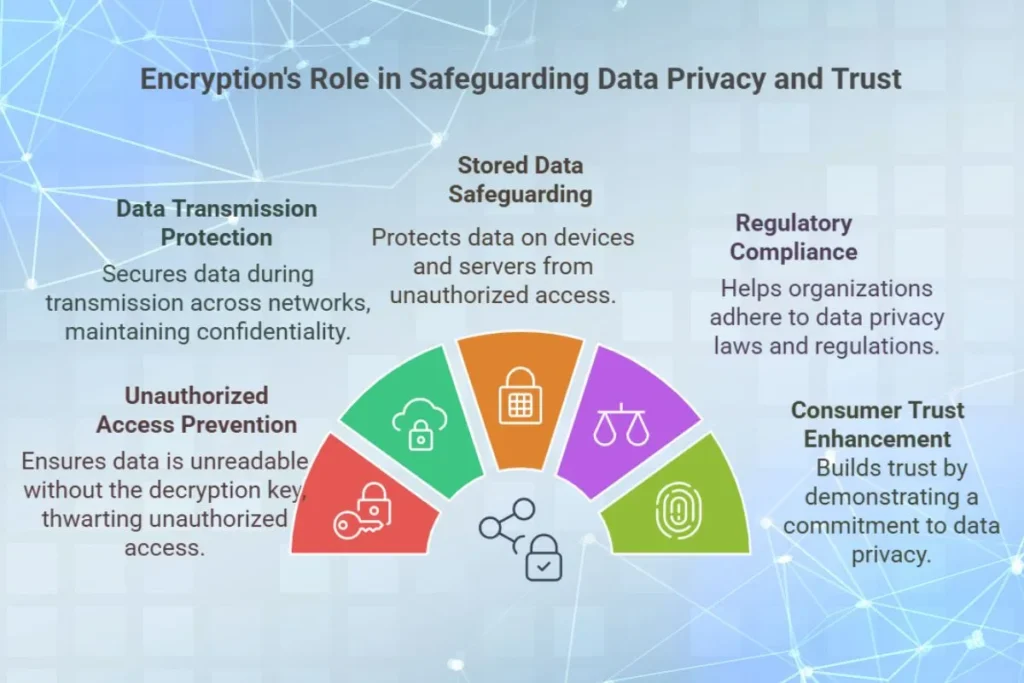
Encryption ensures data privacy by making the information unreadable to anyone who does not possess the decryption key. Here’s how:
Prevents Unauthorized Access
-
- Even if hackers intercept encrypted data, they cannot understand it without the decryption key.
Protects Data During Transmission
-
- Encryption secures data as it travels across networks, ensuring it remains confidential.
- Example: HTTPS encrypts data exchanged between your browser and a website, protecting sensitive transactions like online shopping.
Safeguards Stored Data
-
- Encryption protects data stored on devices, databases, and cloud servers from unauthorized access.
- Example: Full-disk encryption secures files on laptops and smartphones, ensuring that even if a device is stolen, the data remains inaccessible.
Ensures Compliance with Regulations
-
- Encryption helps businesses meet data privacy laws and regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, which require organizations to protect sensitive information.
Enhances Consumer Trust
-
- By using encryption, businesses demonstrate their commitment to data privacy, building trust with customers and stakeholders.
Challenges of Data Encryption
While encryption is a powerful tool, it does come with challenges:
- Key Management
- Losing encryption keys can render data inaccessible, even to authorized users.
- Performance Impact
- Encrypting and decrypting large amounts of data can slow down systems, particularly in high-traffic environments.
- Compatibility Issues
- Not all devices or software support advanced encryption standards, leading to potential integration challenges.
- Misuse of Keys
- If keys are compromised, attackers can decrypt sensitive data, highlighting the importance of secure key management practices.
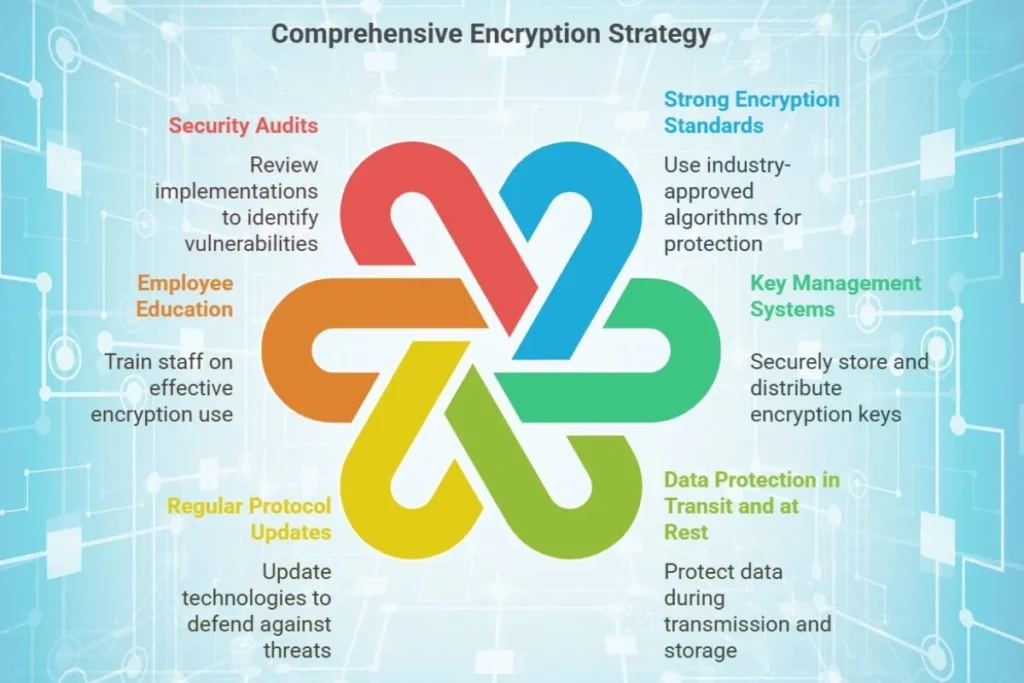
Best Practices for Using Encryption
- Use Strong Encryption Standards
- Stick to industry-approved algorithms like AES-256 or RSA-2048 to ensure robust protection.
- Implement Key Management Systems
- Use secure methods to store, distribute, and manage encryption keys, such as hardware security modules (HSMs).
- Encrypt Both Data in Transit and Data at Rest
- Protect data whether it’s being transmitted over a network or stored on a device, ensuring comprehensive security.
- Update Encryption Protocols Regularly
- Stay updated with the latest encryption technologies to defend against new threats.
- Educate Employees
- Train staff on the importance of encryption and how to use it effectively to prevent accidental data exposure.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits
- Periodically review encryption implementations to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Data encryption is very important in modern cybersecurity. By converting sensitive information into an unreadable format, it ensures data privacy and protects against unauthorized access. Whether you’re a businessman who want to safeguard customer data or an individual who want to secure personal information, encryption is a powerful tool to maintain confidentiality and trust.
Hence, Implement encryption best practices and stay informed about advancements in encryption technologies. This will help you to stay ahead of potential threats and protect your digital assets. With encryption of data, you can create a safer digital environment for everyone.


Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.