The financial institution is the main backbone of any economy, which ensures the secure movement and storage of money, investments and financial data. With the rise of digital banking, online transactions and financial technologies, cybersecurity has become very important to protect sensitive information and prevent fraud.
In this article, we will explore the role of cybersecurity in financial institutions also we will learn the role of cybersecurity in the banking sector, along with the challenges they face and the strategies used to safeguard their operations.
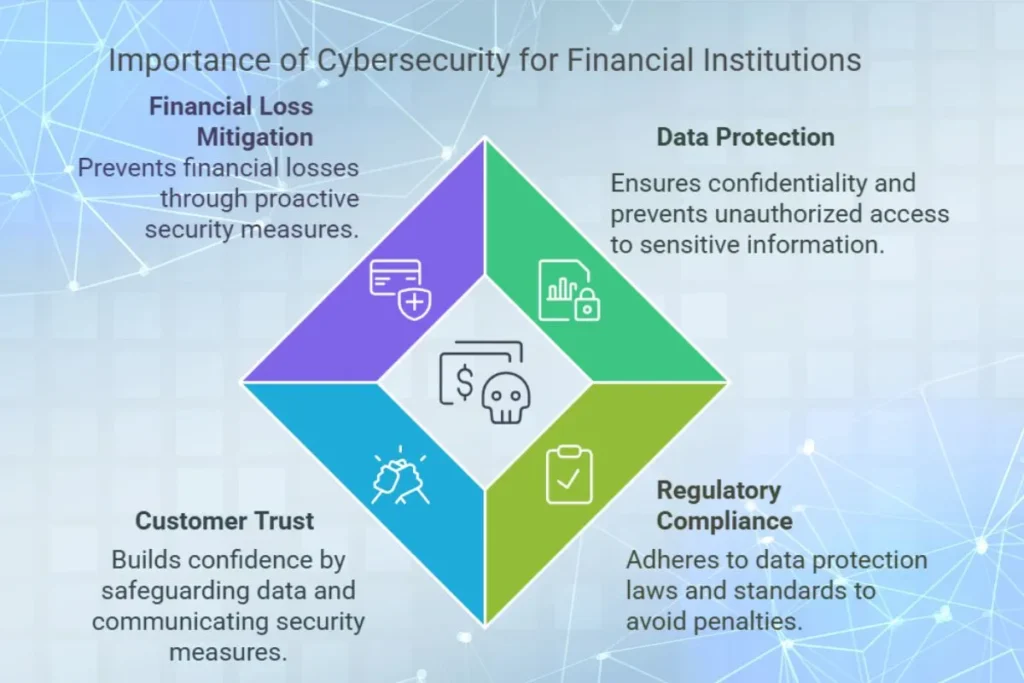
Why Cybersecurity Is Important for Financial Institutions
1. Protection of Sensitive Data
Financial institutions handle vast amounts of sensitive information, including customer data, transaction histories and account details. Cybersecurity ensures this data remains confidential and prevents unauthorized access. For instance, encryption protocols play a crucial role in protecting credit card information during online purchases and banking transfers.
2. Compliance with Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies impose strict data protection laws. Cybersecurity measures help financial institutions comply with standards such as GDPR, PCI DSS and ISO 27001. Regular audits and penetration tests are vital to ensuring compliance and safeguarding against penalties that can arise from data breaches.
3. Building Customer Trust
Trust is essential in the financial industry. Customers expect their data and money to be secure. Strong cybersecurity practices not only protect customers but also enhance the reputation of financial institutions. Institutions that transparently communicate their security measures tend to gain a competitive edge in attracting and retaining customers.
4. Reducing Financial Losses
A single cyberattack can result in significant financial losses due to theft, legal penalties and reputational damage. Cybersecurity minimizes these risks by preventing breaches and ensuring rapid responses. Advanced fraud detection systems, for instance, help prevent millions in potential losses annually by flagging suspicious activities before they escalate.
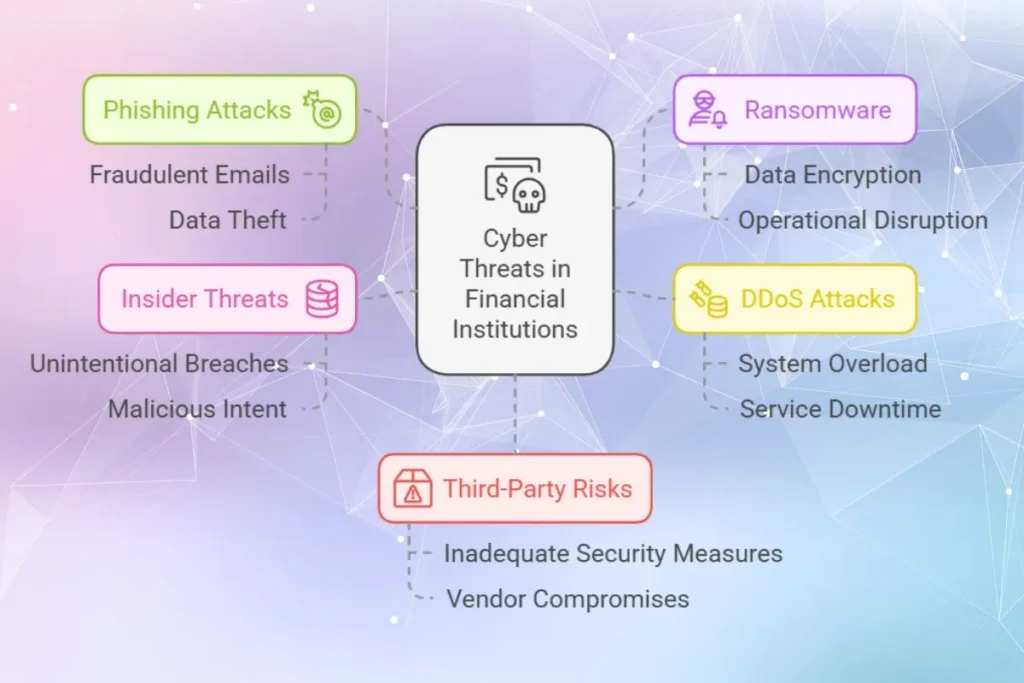
Common Cyber Threats Faced by Financial Institutions
1. Phishing Attacks
Hackers use fraudulent emails or websites to trick employees or customers into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials. For example, phishing schemes have been reported to cause millions of dollars in losses annually by targeting unsuspecting individuals within financial institutions.
2. Ransomware
Ransomware attacks encrypt critical data and hackers demand payment for its release. These attacks can disrupt operations and lead to permanent data loss. A ransomware incident in a regional bank, for instance, resulted in halted services for days and significant reputational damage.
3. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
Hackers overload a bank’s systems with traffic, causing downtime and disrupting online banking services. This type of attack causes inconveniences to the customers and also undermines trust in digital banking platforms.
4. Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with access to sensitive systems can unintentionally or maliciously cause security breaches. For example, leaked employee credentials have been used in cyberattacks that exposed thousands of customer accounts. This highlights the importance of strong internal security protocols.
5. Third-Party Risks
Outsourcing and third-party services introduce vulnerabilities if those providers do not have adequate security measures. A notable example involves a vendor’s compromised software being exploited as a backdoor to access a bank’s internal systems.
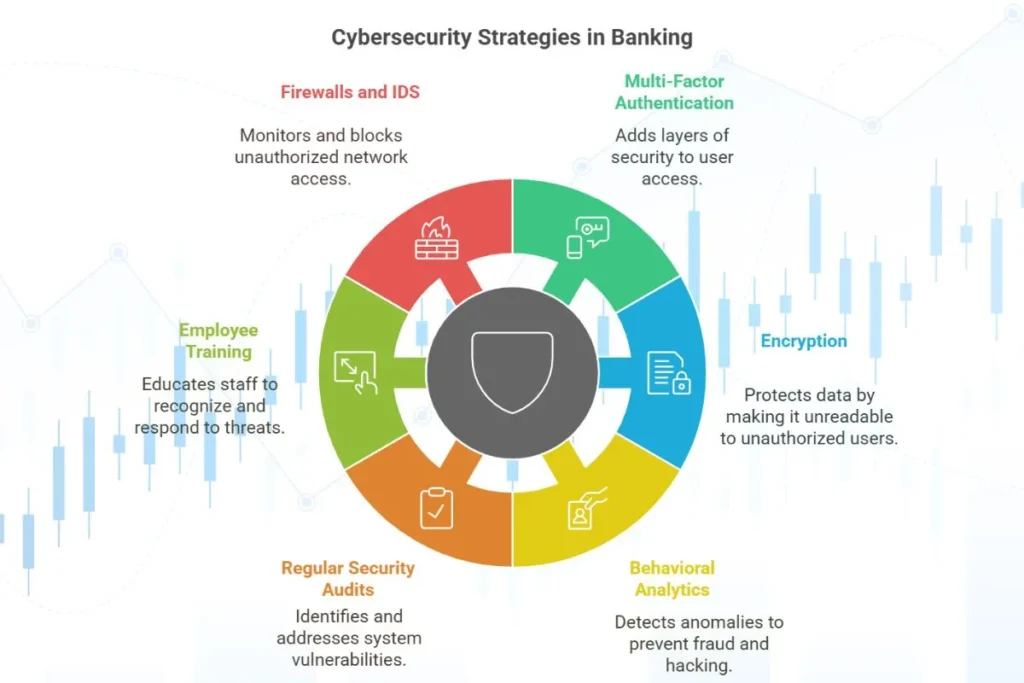
Key Cybersecurity Strategies in the Banking Industry
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA requires users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. This adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if one method is compromised, unauthorized access is prevented.
2. Encryption
Encryption ensures that sensitive data is unreadable to unauthorized users. It is used for data in transit and at rest. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption, for example, protects data during online banking sessions, ensuring transactions remain secure.
3. Behavioral Analytics
AI-powered systems monitor user behavior to detect anomalies that may indicate fraud or hacking attempts. Unusual login locations or transaction patterns can trigger immediate security alerts, enabling proactive responses.
4. Regular Security Audits
Audits identify vulnerabilities in a system and ensure compliance with cybersecurity standards. Annual penetration testing, for instance, reveals weaknesses that can be promptly addressed, ensuring systems remain secure.
5. Employee Training
Employees are the first line of defense. Training programs raise awareness about phishing, password management and recognizing suspicious activities. Simulated phishing campaigns, for example, help employees identify and report fraudulent emails, reducing the risk of successful attacks.
6. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls and IDS monitor and block unauthorized access to networks. Firewalls filter malicious traffic, while IDS detects suspicious activities in real time, ensuring that threats are identified and mitigated promptly.
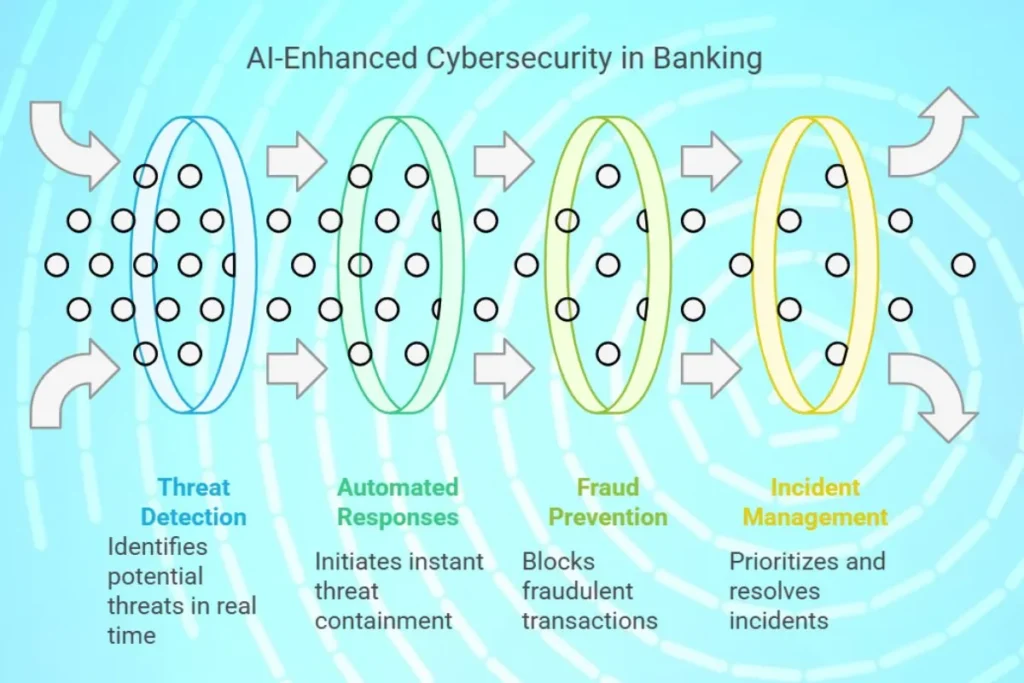
Role of AI in Banking Cybersecurity
1. Threat Detection
AI analyzes vast amounts of data to identify patterns and detect potential threats in real time. For instance, AI systems can flag unusual withdrawal patterns as potential fraud, which prevents unauthorized transactions from occurring.
2. Automated Responses
AI systems can respond to threats instantly, which isolates affected systems and minimizes damage. Automated systems, for example, can block IP addresses involved in brute force attacks, to ensure quick containment.
3. Fraud Prevention
Machine learning algorithms identify and prevent fraudulent transactions by analyzing transaction histories and behaviors. AI systems that detect unusual spending patterns deviating from a customer’s normal behavior, this helps to reduce frauds effectively.
4. Improved Incident Management
AI helps to prioritize and manage incidents based on their severity, which ensures critical issues are resolved promptly. By streamlining the incident reporting process, AI reduces resolution times and enhances the overall security posture of financial institutions.
Challenges in Implementing Cybersecurity
1. Evolving Threat Landscape
Cybercriminals continuously develop new methods to bypass security measures, which requires constant updates and alertness. Zero day vulnerabilities, for instance, exploit unpatched systems before security teams can respond, this poses significant risks.
2. Cost of Implementation
Advanced cybersecurity tools and skilled personnel are expensive, especially for smaller financial institutions. This financial burden makes it challenging for smaller banks to adopt state of the art security systems, which increases their risk of exposure to threats.
3. Balancing Security and User Experience
Excessive security measures can inconvenience customers, leading to dissatisfaction. For example, lengthy authentication processes may deter customers from using digital services. Hence there is need for a balanced approach.
4. Third-Party Dependencies
Relying on external vendors increases risks if their systems are compromised. A compromised third-party vendor’s software, for instance, allowed attackers to access sensitive data indirectly, emphasizing the importance of vetting third-party providers.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is very essential for financial institutions and the banking sector. It protects sensitive data, builds customer trust and prevents financial losses. With the integration of advanced technologies like AI, banks can stay ahead of evolving threats. However, challenges such as cost and an ever growing cyber threats require continuous effort and innovation.
By giving priority to cybersecurity, financial institutions can ensure a secure and trustworthy environment for their customers and maintain operational efficiency in this competitive world.

