Artificial intelligence (AI) has brought revolution in the job market by automating tasks, improving efficiency and creating new job opportunities. Although, AI enhances productivity, it also raises concerns about job displacement.
One question is always asked, how does artificial intelligence impact jobs? How does AI affect jobs? Workers, employers and policymakers must understand the impact of IT on job market to prepare for the future.
Effect of Artificial Intelligence on Job Market
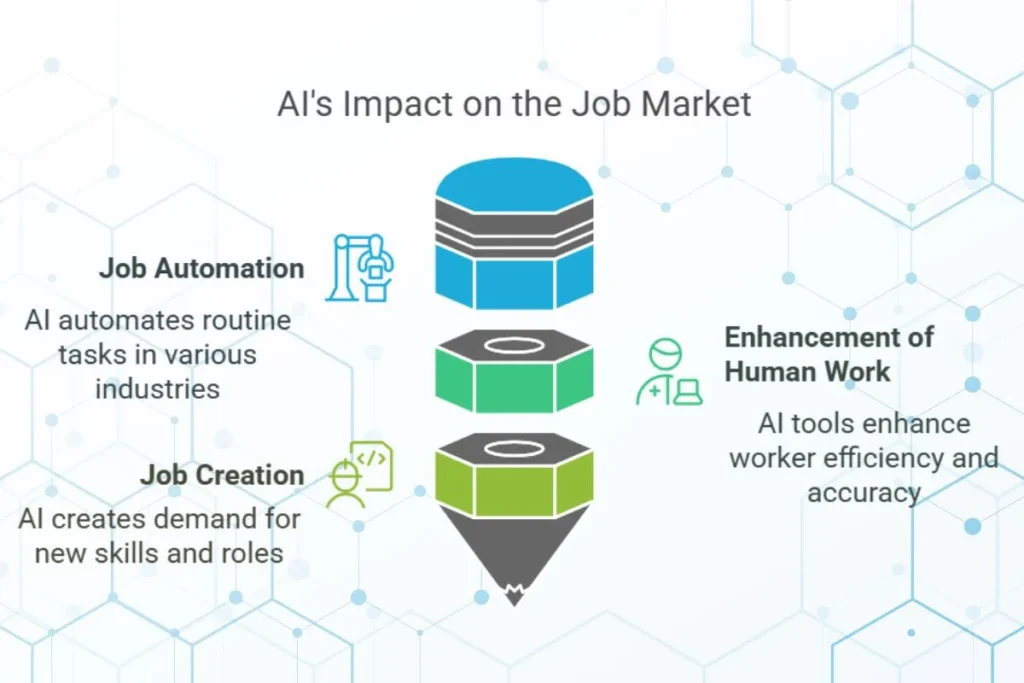
As AI is progressing, the job scenario is changing in three major ways:
- Automating Repetitive Tasks – AI handles routine and manual tasks, which reduces the need for human effort.
- Enhancing Human Work – AI tools support workers, which improves speed and accuracy.
- Creating New Job Opportunities – AI creates demand for new skills and industries.
1. AI and Job Automation
AI automates tasks that have repetitive processes and structured decision making procedure. Industries relying on manual labor and predictable workflows are looking for the biggest impact.
Industries Affected by AI Automation:
- Manufacturing: AI powered robots assemble products, which reduces labor costs.
- Retail: Self checkout systems and AI driven inventory management optimize store operations.
- Customer Service: AI chatbots handle inquiries, which reduces the need for human agents.
- Transportation: Self driving vehicles and automated logistics streamline deliveries.
- Finance: AI algorithms detect fraud and process transactions instantly.
Example:
Amazon uses AI driven robots to move inventory in warehouses. This increases efficiency but also shifts job roles toward technical maintenance and AI system management.
2. AI as a Tool for Workers
AI is not just replacing jobs, but it is also enhancing them. Many industries use AI to assist workers in completing tasks more efficiently.
Ways AI Supports Workers:
- Healthcare: AI analyzes medical scans and assists doctors to diagnose diseases.
- Education: AI tutors provide personalized learning experiences.
- Marketing: AI processes customer data to improve targeted advertising.
- Software Development: AI detects errors and suggests code improvements.
Example:
IBM Watson AI helps doctors to analyze medical records, and suggests treatment options. This allows healthcare professionals to make better decisions.
3. AI and Job Creation
AI is generating new job opportunities. Many companies now hire AI specialists to design, develop and manage AI systems.
New Jobs Created by AI:
- AI Engineers and Developers
- Data Scientists
- AI Ethics Specialists
- Automation Experts
- Cybersecurity Analysts
- AI Trainers and Maintenance Technicians
Example:
The demand for AI professionals is growing rapidly. Tech companies like Google, Tesla and Microsoft are hiring AI specialists to build cutting edge solutions.
The Impact of AI on Different Job Sectors
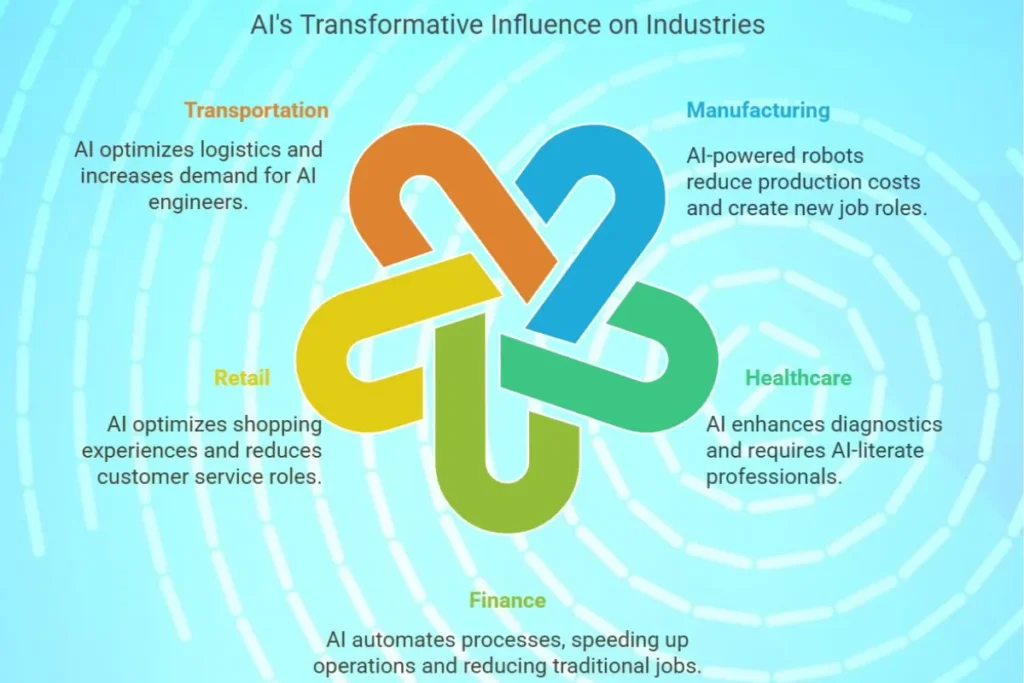
AI affects industries in different ways. Some sectors experience major automation, while others see AI technology is improving efficiency and decision making process.
1. AI in Manufacturing
AI powered robots perform repetitive tasks in assembly lines, which reduces production costs.
- Impact: Fewer manual jobs, but more demand for AI system managers and maintenance workers.
2. AI in Healthcare
AI assists doctors to diagnose diseases and analyze medical images.
- Impact: Better patient care, but greater demand for AI literate medical professionals.
3. AI in Finance
AI automates fraud detection, risk analysis and customer service operations.
- Impact: Faster financial processes, but reduced need for traditional banking jobs.
4. AI in Retail
AI recommendation engines improve shopping experiences and optimize inventory.
- Impact: More personalized shopping, but it will reduce customer service roles and jobs
5. AI in Transportation
Self driving vehicles and AI powered logistics optimize routes and deliveries.
- Impact: Fewer traditional driving jobs, but increased demand for AI engineers.
Challenges of AI in the Job Market
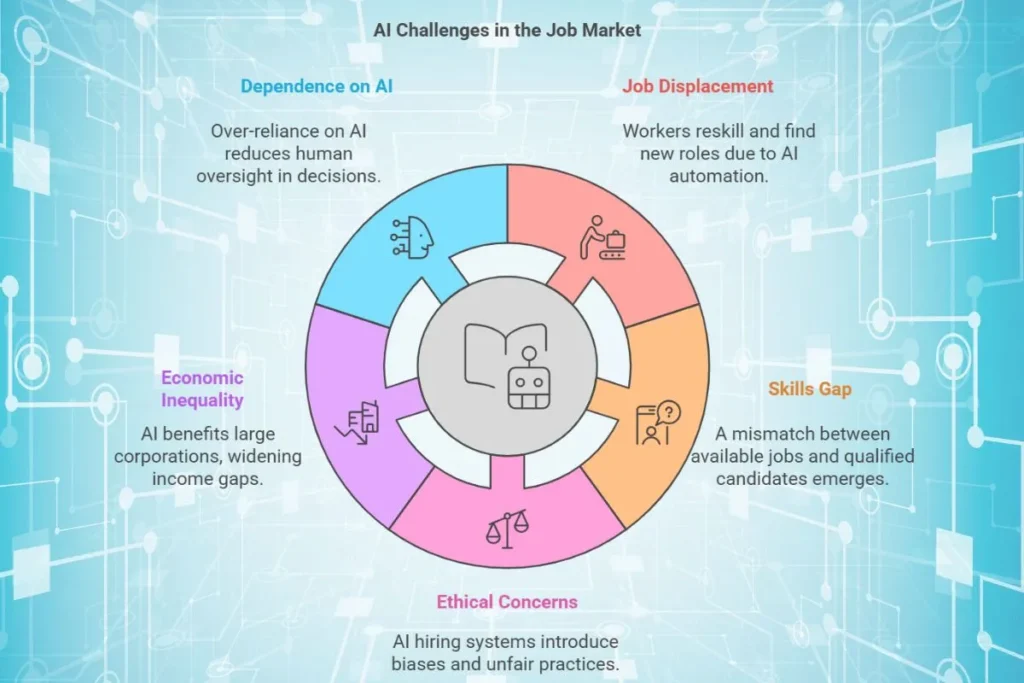
AI has many advantages, but it also presents challenges that businesses and workers must solve.
1. Job Displacement
AI automation may reduce demand for some jobs, which forces workers to reskill and find new roles.
2. Skills Gap
Many workers lack AI related skills, which creates a gap between available jobs and qualified candidates.
3. Ethical Concerns
AI driven hiring systems may introduce biases, which leads to unfair employment practices.
4. Economic Inequality
Large corporations benefit more from AI than small businesses, which potentially widens the income gaps.
5. Dependence on AI
Over reliance on AI could reduce human oversight in important decision making areas.
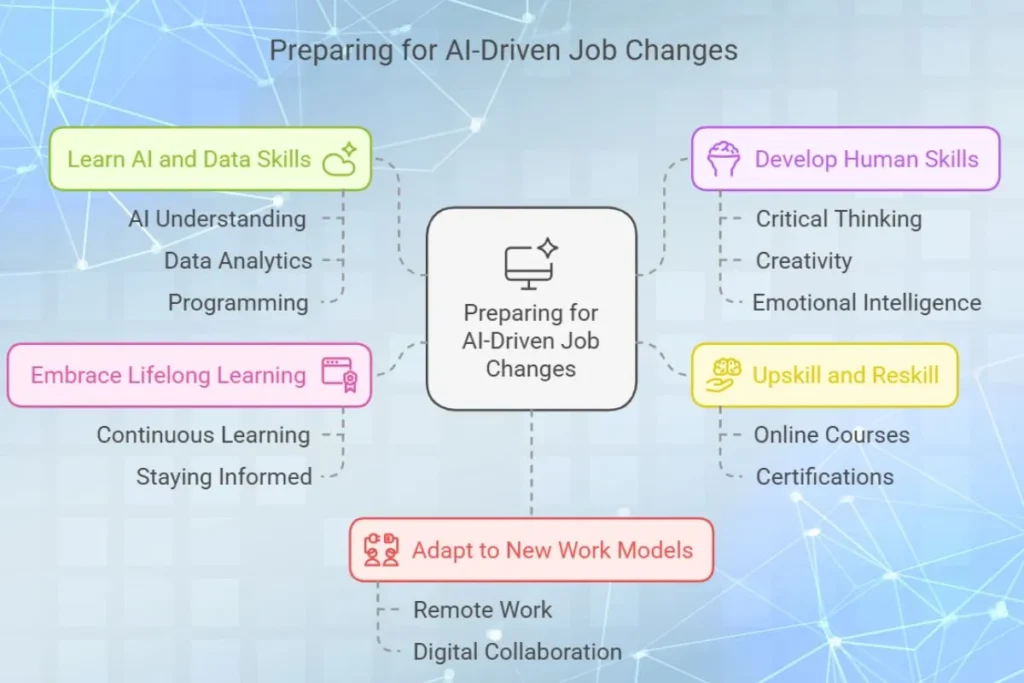
How to Prepare for Job Changes due to AI
Workers need to adapt to AI technologies by learning new skills and staying informed about emerging technologies.
1. Learn AI and Data Skills
Understanding AI, data analytics and programming can open up new career paths.
2. Develop Human Skills
Critical thinking, creativity and emotional intelligence remain valuable, as AI cannot replicate these qualities.
3. Upskill and Reskill
Online courses and certifications in AI related fields help workers to transition into new roles.
4. Embrace Lifelong Learning
Continuous learning ensures workers to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving job market.
5. Adapt to New Work Models
Remote work and digital collaboration are increasing, which requires workers to be flexible and tech savvy.
Key Takeaways:
- AI automates repetitive tasks, but it also enhances human work.
- AI creates new job opportunities in tech, data science and automation.
- Workers must develop AI related skills to remain competitive.
- Human qualities like creativity and problem solving attitude remain irreplaceable.
Conclusion
AI will continue to transform jobs, but human skills will remain always essential. AI will restructure industries rather than eliminate jobs entirely. Workers who adapt and develop new skills will have better career opportunities in this AI dominated world.
The future of jobs depends on how businesses, governments and workers adapt to AI. Technology will continue to evolve, but human innovation and adaptability will always play a central role in shaping the workforce of the future.

