We read in newspaper about ‘data breaches’. Many people ask, how does cybersecurity protect data? how does cybersecurity protect against data breaches? As we know, in this digital world where data is a very important asset, protecting it has become more important than ever. Cybersecurity plays a important role in safeguarding data and preventing data breaches.
This article explores how does cybersecurity protect against data breaches and the various strategies it employs to defend against unauthorized access. We will also discuss about the challenges organizations face and the best practices they can adopt to enhance data security.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the measures and practices designed to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. These threats include hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. Cybersecurity aims to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, often referred to as the CIA triad.
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that data is accessible only to authorized users.
- Integrity: Protecting data from being altered or tampered with.
- Availability: Ensuring that data and systems are accessible when needed.
Cybersecurity encompasses a wide range of technologies, processes, and policies, making it a cornerstone of modern information security.
How Cybersecurity Protects Data
Cybersecurity uses a combination of tools, technologies, and best practices to safeguard data. Below are some key ways it ensures data protection:
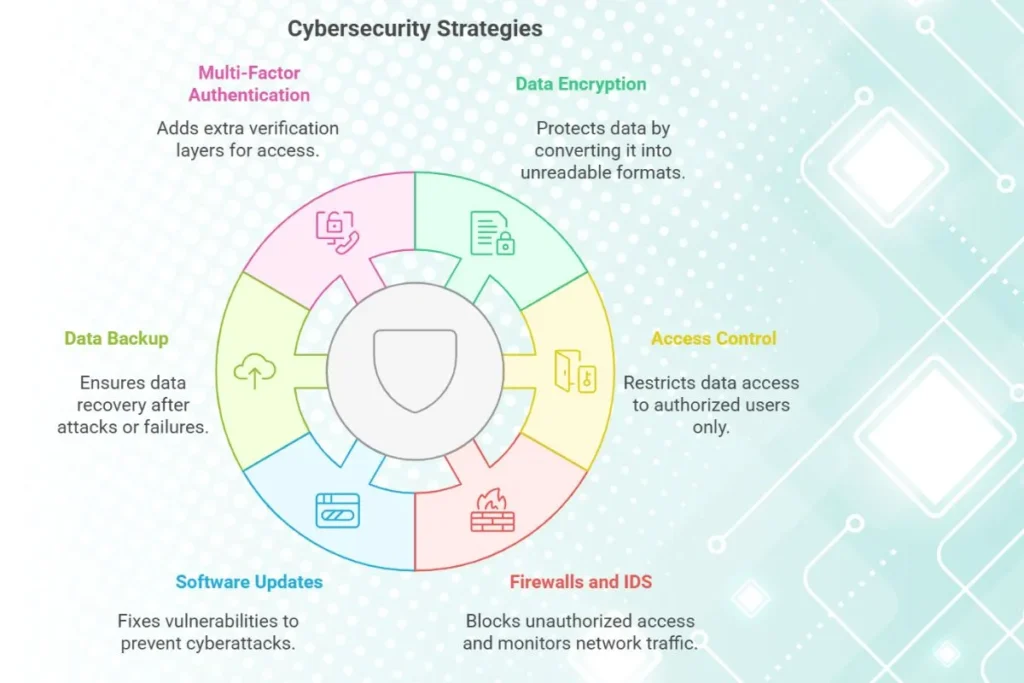
1. Data Encryption
Encryption converts data into an unreadable format that can only be decoded with a decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible to unauthorized users.
- Example: Online banking transactions use encryption to secure sensitive information like account numbers and passwords.
2. Access Control
Access control mechanisms ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific data or systems. This includes user authentication and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Example: Employees in a company may have access only to the data relevant to their role.
3. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls act as barriers between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks, while IDS monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Example: A firewall may block unauthorized attempts to access a company’s database.
4. Regular Software Updates and Patches
Outdated software can contain vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit. Regular updates and patches fix these vulnerabilities and strengthen security.
- Example: Companies using outdated operating systems are at higher risk of ransomware attacks.
5. Data Backup
Regularly backing up data ensures that it can be recovered in case of a cyberattack, hardware failure, or accidental deletion.
- Example: A company’s cloud backup system can restore files encrypted by ransomware.
6. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access.
- Example: Logging into an email account may require both a password and a one-time code sent to a phone.
How Cybersecurity Prevents Data Breaches
Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals access sensitive information. Cybersecurity strategies aim to prevent breaches by addressing vulnerabilities and proactively defending against threats. Here’s how:
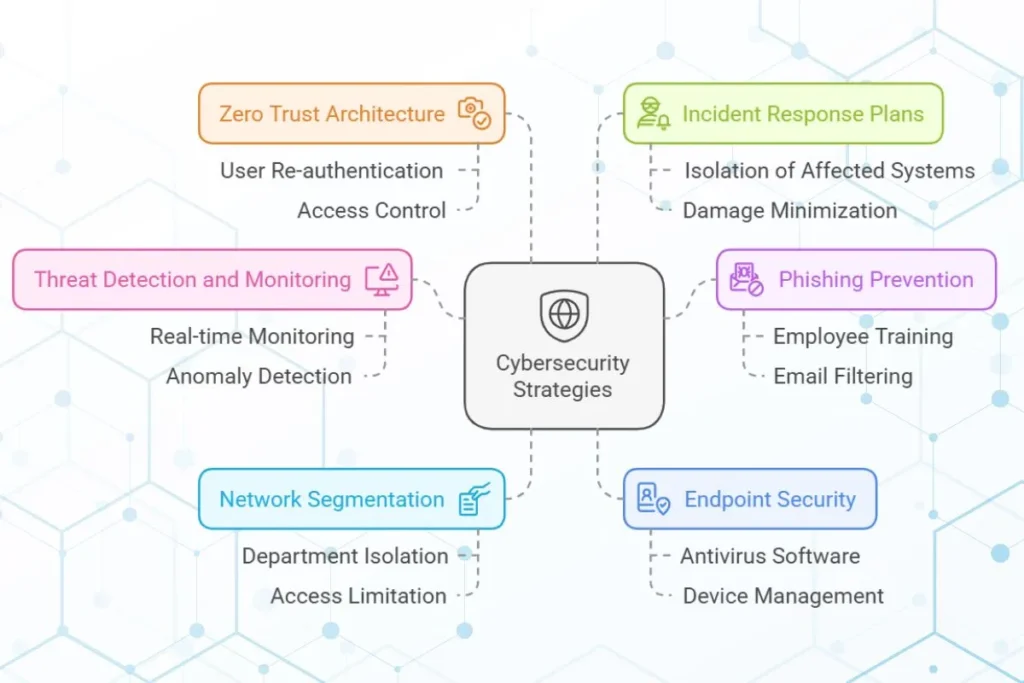
1. Threat Detection and Monitoring
Advanced monitoring tools detect unusual activity in real-time, allowing organizations to respond quickly to potential breaches.
- Example: A sudden spike in login attempts could signal a brute-force attack.
2. Phishing Prevention
Cybersecurity includes training employees to recognize phishing attempts and implementing email filters to block malicious emails.
- Example: A phishing email disguised as a message from a bank can be flagged and blocked.
3. Network Segmentation
Segmenting a network into smaller sections limits the impact of a breach by containing the attacker’s access.
- Example: A breached user account in one department cannot access data from another department.
4. Endpoint Security
Protecting devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets prevents attackers from using them as entry points into a network.
- Example: Antivirus software and device management tools secure endpoints against malware.
5. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust assumes that no user or device is trustworthy by default. Verification is required at every step, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Example: A user must re-authenticate before accessing sensitive files, even within a secured network.
6. Incident Response Plans
Having a detailed incident response plan helps organizations react quickly and effectively to data breaches, minimizing damage.
- Example: An incident response team isolates affected systems to prevent further data leakage.
Real-World Examples
1. Equifax Data Breach (2017)
One of the largest breaches in history, the Equifax breach exposed personal data of over 147 million people. The breach occurred due to unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Lesson: Regular software updates and patch management are critical for preventing breaches.
2. Target Data Breach (2013)
Hackers gained access to Target’s network through a third-party vendor, compromising the credit card information of millions of customers.
- Lesson: Third-party risk management is essential for data security.
3. SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack (2020)
This sophisticated attack infiltrated numerous organizations, including government agencies, by exploiting vulnerabilities in software updates.
- Lesson: Supply chain security and monitoring third-party software are critical to cybersecurity.
Challenges in Cybersecurity
While cybersecurity is essential, it comes with its challenges:
- Evolving Threat Landscape
- Cyber threats are constantly changing, requiring organizations to stay updated.
- Resource Constraints
- Small businesses may lack the budget or expertise for robust cybersecurity.
- Human Error
- Employees can inadvertently cause security breaches through negligence or lack of awareness.
- Complex Systems
- Managing and securing large, interconnected systems can be daunting.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity
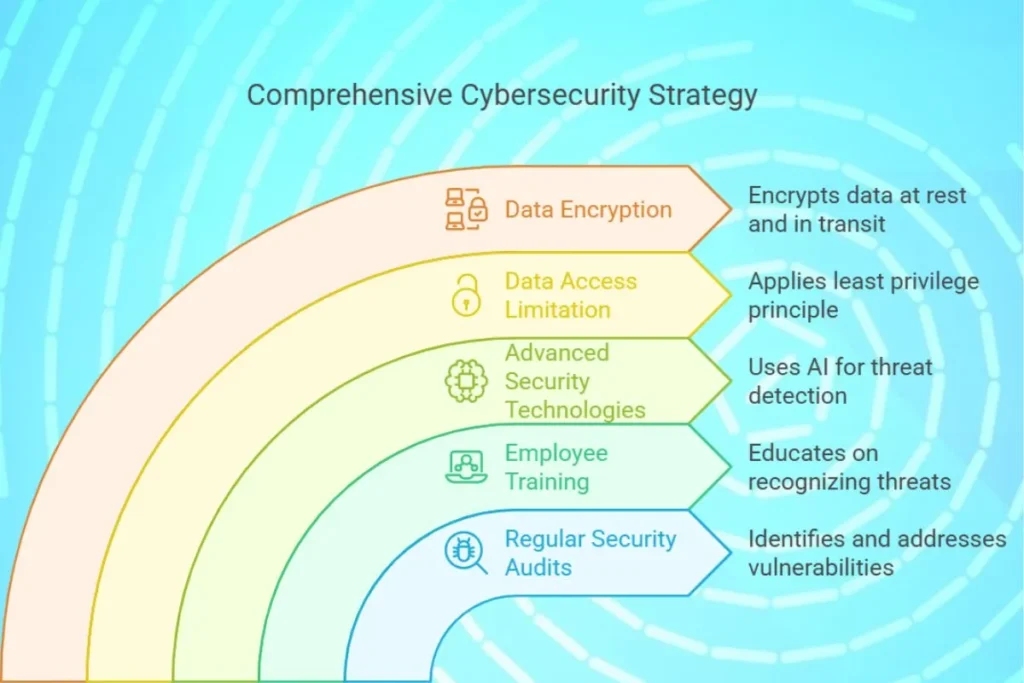
1. Conduct Regular Security Audits
- Identify vulnerabilities and address them promptly.
2. Implement Employee Training
- Teach employees to recognize threats like phishing and social engineering.
3. Adopt Advanced Security Technologies
- Use AI-driven threat detection and automated responses.
4. Limit Data Access
- Apply the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to restrict data access.
5. Encrypt Sensitive Data
- Ensure all sensitive information is encrypted, both at rest and in transit.
6. Develop Incident Response Plans
- Have a clear plan to contain and recover from breaches.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is essential for protecting data and preventing breaches in today’s day to days digital life. By combining technologies, best practices and employee awareness, organizations can safeguard their valuable information and maintain customer trust.
Methods like encrypting data, monitoring for threats or training staff, are a proactive approach to cybersecurity and the key to prevent breaches and ensure data privacy. Hence invest in strong cybersecurity measures and protect yourself along with your organization against data breaches.

