Emails are a important part of communication, but they can also be a gateway for cybercriminals to penetrate into your personal or professional life. How to identify an unsafe email is very crucial. Dangerous emails, such as phishing attempts or those containing malware, can compromise sensitive information, which leads to financial loss or disrupts business operations. Hence internet security is very much important.
This blog will teach you how to identify a dangerous email and provide essential tips for cybersecurity to protect yourself and your organization.
Why Recognizing Dangerous Emails is Important
Cybercriminals often mask malicious emails to look legitimate. Clicking on a harmful link or downloading an infected attachment can lead to:
- Data breaches: Exposing sensitive data to attackers.
- Financial loss: Unauthorized access to bank accounts or fraudulent transactions.
- Reputational damage: Loss of trust from customers or colleagues.
- System compromise: Malware or ransomware infections that disrupt operations.
Knowing how to spot red flags can help you avoid these consequences.
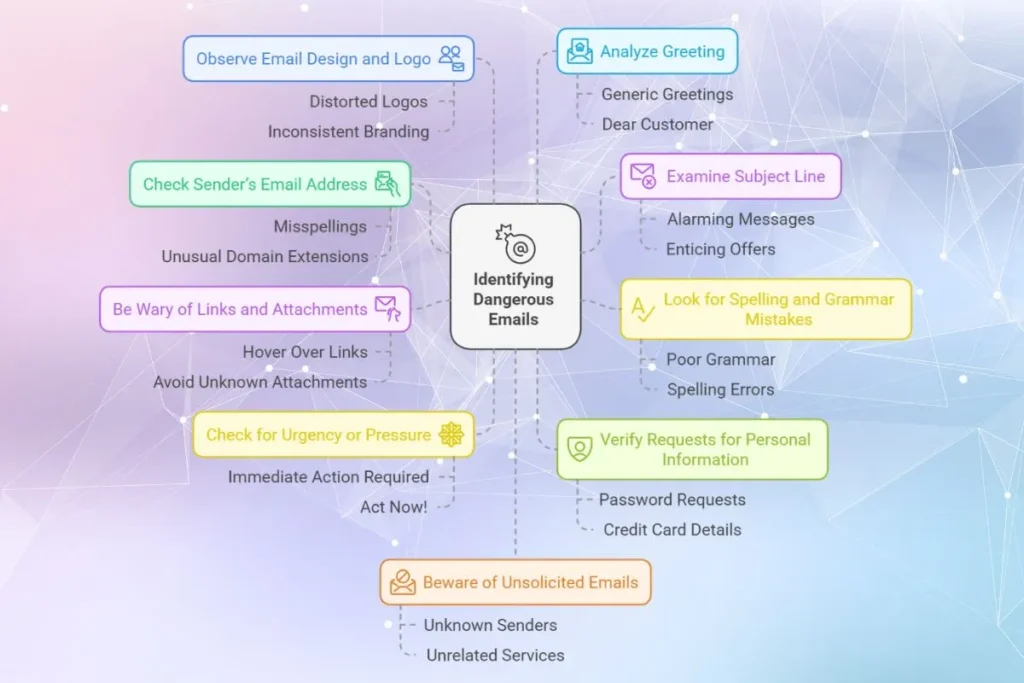
How to Identify a Dangerous Email
1. Check the Sender’s Email Address
Always verify the sender’s email address. Cybercriminals often use email addresses that look similar to legitimate ones.
- Example: A genuine email might be from “support@amazon.com,” while a fake one could be “support@amaz0n.com.”
- Look for slight changes like misspellings or unusual domain extensions (e.g., “.co” instead of “.com”).
2. Examine the Subject Line
Suspicious emails often use alarming or enticing subject lines to grab attention.
- Examples include:
- “Your account has been suspended!”
- “You’ve won $1,000,000!”
- “Urgent action required!”
Legitimate organizations rarely use such tactics.
3. Look for Spelling and Grammar Mistakes
Professional organizations ensure their emails are free of errors. Poor grammar or spelling mistakes are common in fraudulent emails.
- Example of a phishing email:
“Dear cust0mer, We notice unusual activitty on your account. Please clikc here to update your informations.”
4. Be aware of Links and Attachments
Dangerous emails often contain malicious links or attachments.
- Hover over links: Place your cursor over a link to see the actual URL before clicking. If it looks suspicious or unrelated, do not click.
- Avoid unknown attachments: Files like .exe, .zip, or .docx can contain malware.
5. Check for Urgency or Pressure
Scammers often create a sense of urgency to make you act without thinking.
- Phrases like “Act now!” or “Immediate action required!” are common.
- Legitimate organizations usually provide adequate time for responses and do not use scare tactics.
6. Verify Requests for Personal Information
Legitimate companies rarely ask for sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, via email.
- Example of a phishing attempt:
“Your account has been compromised. Enter your username and password here to secure it.”
If in doubt, contact the organization directly using official contact details.
7. Observe the Email Design and Logo
Fake emails often have poor design quality or distorted logos. Legitimate companies maintain consistent branding in their emails.
- Check for mismatched fonts, low-resolution images, or irregular layouts.
8. Analyze the Greeting
Legitimate emails typically address you by name, while phishing emails use generic greetings.
- Example of a suspicious greeting:
- “Dear Customer,” or “Hello User.”
9. Beware of Unsolicited Emails
If you receive an email from an unknown sender or regarding a service you never signed up for, it’s likely fraudulent.
- Example: Receiving an email about a lottery you never entered.
10. Look for Security Features
Legitimate emails often include security features like a digital signature or a verified sender mark (e.g., “via” a known domain).
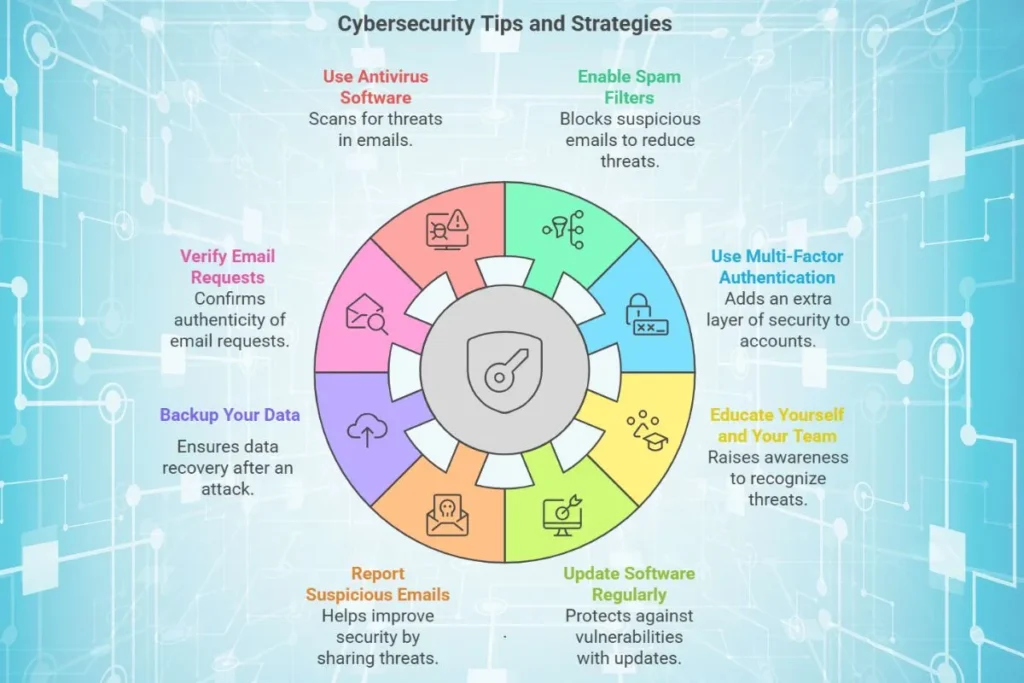
Essential Tips for Cybersecurity
To stay safe from dangerous emails, follow these best practices:
1. Enable Spam Filters
Most email providers have spam filters that block suspicious emails. Keep these filters activated and updated.
2. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi Factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. Even if an attacker gets your credentials, MFA makes it harder to access your account.
3. Educate Yourself and Your Team
Regular training on cybersecurity awareness helps employees recognize and avoid dangerous emails. Inform your team latest trends in cybersecurity and new threats and new methods of cyber attack.
4. Update Software Regularly
Outdated email clients or operating systems are more vulnerable to attacks. Install updates promptly.
5. Report Suspicious Emails
Most email platforms allow you to report phishing attempts. This helps improve security for everyone. Always use the feature “Report Spam” for a spam email to alert the concerned provider.
6. Backup Your Data
Regular backups your precious data to ensure that, you can recover your data if an attack occurs.
7. Verify Email Requests
If you’re unsure about an email’s authenticity, contact the sender directly using verified contact details or other mode of communication.
8. Use Antivirus Software
Install reliable antivirus software to scan email attachments and links for threats. Periodically scan your PC for any malware or threats.
Real-World Examples
Case Study: CEO Fraud
An employee at a company received an email that appeared to be from their CEO, asking for a wire transfer. The scammer used a similar email address and urgent language. The employee sent the money before realizing it was a scam.
Lesson: Always verify financial requests through a secondary communication channel, like a phone call.
Case Study: Fake Invoice Scam
A small business received an email with a fake invoice attachment. The attachment contained malware that encrypted all company data, leading to a ransomware demand.
Lesson: Avoid downloading attachments from unknown sources.
Key Takeaways
- Always verify email senders and scrutinize links and attachments.
- Educate yourself and your team to recognize phishing attempts.
- Use cybersecurity tools like antivirus software, spam filters and MFA.
- Report suspicious emails to your email provider or IT department.
Conclusion
Dangerous emails pose a significant risk to personal and organizational security. By learning how to identify them and implementing strong cybersecurity practices, you can protect your sensitive information and avoid costly breaches.
Stay alert, educate other co-workers and colleagues and give priority to security in your daily email interactions.

