Data privacy, also known as information privacy, refers to the proper handling, processing, storage and usage of personal data. It ensures that sensitive information, such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, financial details and browsing habits, is protected. One must know, as what is data privacy and the right of data privacy that gives them control over how their information is collected, shared and used. One question often arises as how to protect data privacy in the age of social media.
Data privacy has become more important with the increasing digitization of personal and professional interactions. Whether you are signing up for a new social media account, shopping online, or simply browsing the internet, your data is constantly being collected.
What is Data Privacy and why it is Important?
In this interconnected world, personal data has became more valuable. Businesses use it for targeted advertising, governments use it for security and cybercriminals use it for exploitation. A breach of data privacy can lead to identity theft, financial loss, reputational harm and legal issues.
Moreover, data privacy is about protecting human rights. Unauthorized data access can lead to discrimination, surveillance and loss of freedom. For instance, leaked financial data might be used by scammers to exploit unsuspecting individuals. On a larger scale, compromised government or corporate data can have severe economic and social consequences.
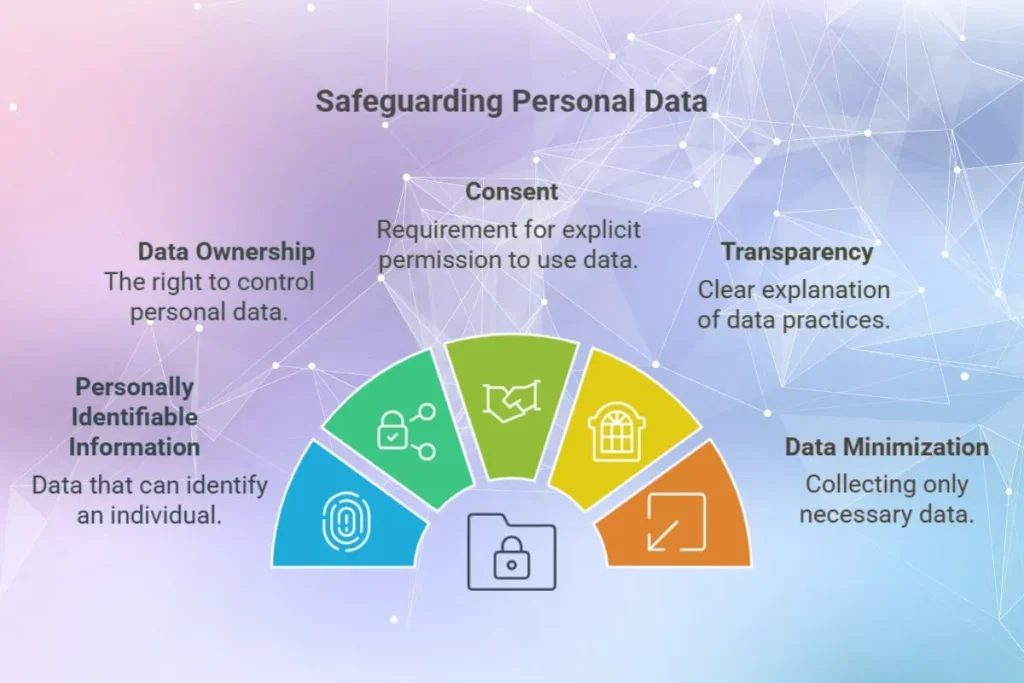
Key Concepts of Data Privacy
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Any data that can identify an individual, such as a name, Social Security number or email address.
- Data Ownership: The individual’s right to control their personal data.
- Consent: The requirement for explicit user permission to collect or use their data.
- Transparency: Organizations must clearly explain how they collect, store and use personal data.
- Data Minimization: Only necessary data should be collected and stored to reduce risk.
- Accountability: Companies and organizations must take responsibility for safeguarding the data they collect and ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
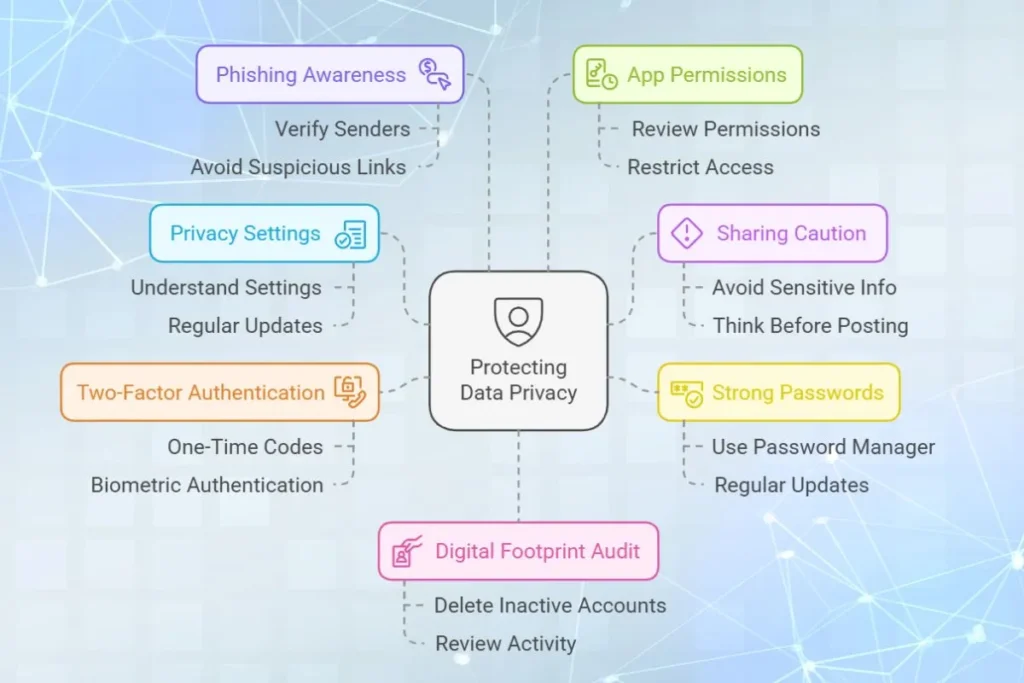
Protecting Data Privacy in the Age of Social Media
Social media has revolutionized communication but also introduced new risks to personal data. Here are actionable steps to safeguard your privacy:
1. Understand Social Media Privacy Settings
Every platform provides privacy settings to control who can access your posts, profile and personal details.
- Example: On Facebook, you can limit your profile visibility to “Friends Only.”
- Tip: Regularly review and update your privacy settings for maximum security. Platforms often update their privacy policies and settings, so always stay informed.
2. Be Cautious About What You Share
Avoid posting sensitive information like:
- Home or office addresses
- Phone number, e-mail address etc.
- Financial details
Example: Cybercriminals could use vacation photos to know when your home is empty. Even innocent posts like celebrating a birthday might reveal personal information that can be exploited.
3. Use Strong Passwords
Strong passwords are very important for protecting your accounts. A good password should:
- Be at least 12 characters long.
- Include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols.
- Avoid predictable patterns like “123456” or “password.”
Tip: Use a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords. Regularly updating your passwords can also minimize the risk.
4. Enable Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two factor authentication adds an additional layer of security by requiring a second step to log in. For example:
- A one time code sent to your mobile device.
- Biometric authentication like fingerprint or facial recognition.
Tip: Enable 2FA on all major accounts, including social media, email and banking apps.
5. Be Aware of Phishing Attempts
Phishing scams trick users into sharing personal information. These scams often come in the form of:
- Emails claiming to be from trusted organizations.
- Fake websites designed to steal login credentials.
Example: A scam email might mimic your bank, asking you to “verify your account” by entering sensitive information on a fake site.
Tip: Always verify the sender’s identity and avoid clicking on suspicious links. Use official websites or apps to log in directly.
6. Limit App Permissions
Mobile apps often request access to data that isn’t necessary for their function. For example:
- A flashlight app asking for location access.
- A game requesting access to your contacts.
Tip: Review and restrict app permissions in your device settings. Only allow access to what’s essential for the app to function.
7. Regularly Audit Your Digital Footprint
Your digital footprint includes all the data you leave behind online. This can include:
- Old social media posts.
- Unused accounts.
Tip: Delete inactive accounts and unnecessary posts. Use tools like Google’s “My Activity” to review and manage your online activity.
Real-World Examples of Data Privacy Breaches
- Facebook-Cambridge Analytica Scandal (2018): This breach exposed how data from millions of users was harvested without consent and used for political advertising.
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): Over 147 million Americans had their personal information, including Social Security numbers, compromised.
- Yahoo Data Breach (2013-2014): A breach affecting all 3 billion Yahoo accounts, compromising email addresses, passwords, and security questions.
Lessons Learned:
- Even large organizations can fail to protect data adequately.
- Users must take personal responsibility for securing their information.
Data Privacy Laws and Regulations
Governments worldwide are enacting laws to protect personal data. Key regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enacted in the European Union, it gives individuals greater control over their data and imposes strict penalties for non-compliance.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Provides California residents the right to know how their data is collected and shared.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Protects sensitive health information in the U.S.
Tip: Familiarize yourself with data privacy laws applicable to your region. These laws can help you understand your rights and hold organizations accountable.
Conclusion
Data privacy is not just a technical issue; it’s a fundamental human right. In the age of social media and digital connectivity, protecting your personal information requires alertness and proactive measures. By understanding the risks and adopting best practices like using strong passwords, enabling 2FA and limiting data sharing, you can significantly enhance your online privacy.
Remember, your data is valuable. Treat it with the same care as you would your most precious objects. Stay informed, stay cautious and stay protected always.

