Now a days, information is one of the most valuable assets for businesses. Protecting this information is essential to ensure business continuity, maintain customer trust and comply with legal regulations. This is where information security and well defined information security policies come into play. Let us understand what is information security; and what are the information security policies for businesses.
What is Information Security?
Information security, often abbreviated as InfoSec, refers to the practice of protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. This includes safeguarding both digital and physical information. The goal is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) of data:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals.
- Integrity: Ensuring that information is accurate and has not been altered without authorization.
- Availability: Ensuring that information is accessible when needed by authorized users.
Businesses handle various types of sensitive information, including customer data, employee records, intellectual property and financial details. Failing to protect this information can lead to financial losses, reputational damage and legal consequences. Moreover, the rise in cyberattacks highlights the importance of robust information security measures to counter these growing threats effectively.
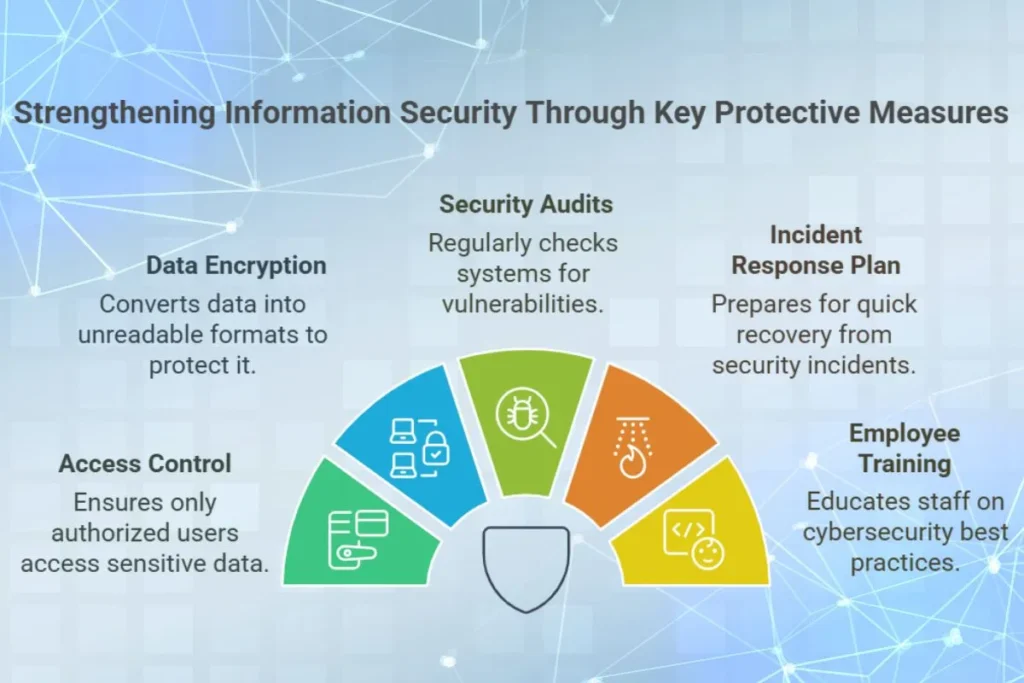
Key Components of Information Security
Access Control
Restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions. Tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) help ensure that only authorized users can access specific information.
Data Encryption
Protect data by converting it into an unreadable format using encryption algorithms. Encryption is essential for securing data in transit and at rest. For instance, end-to-end encryption in messaging apps ensures that only the intended recipients can read the messages.
Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular audits to identify vulnerabilities in your IT systems and address them proactively. Audits provide a comprehensive overview of your organization’s security posture and help prioritize necessary improvements.
Incident Response Plan
Prepare a plan to respond to security incidents, such as data breaches or cyberattacks, to minimize their impact and recover quickly. Having a clear step-by-step guide ensures faster and more effective responses during a crisis.
Employee Training
Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and creating strong passwords. Regular training ensures that employees remain vigilant and act as the first line of defense against cyber threats.
Network Security
Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-virus software to protect your network from unauthorized access and malicious software.
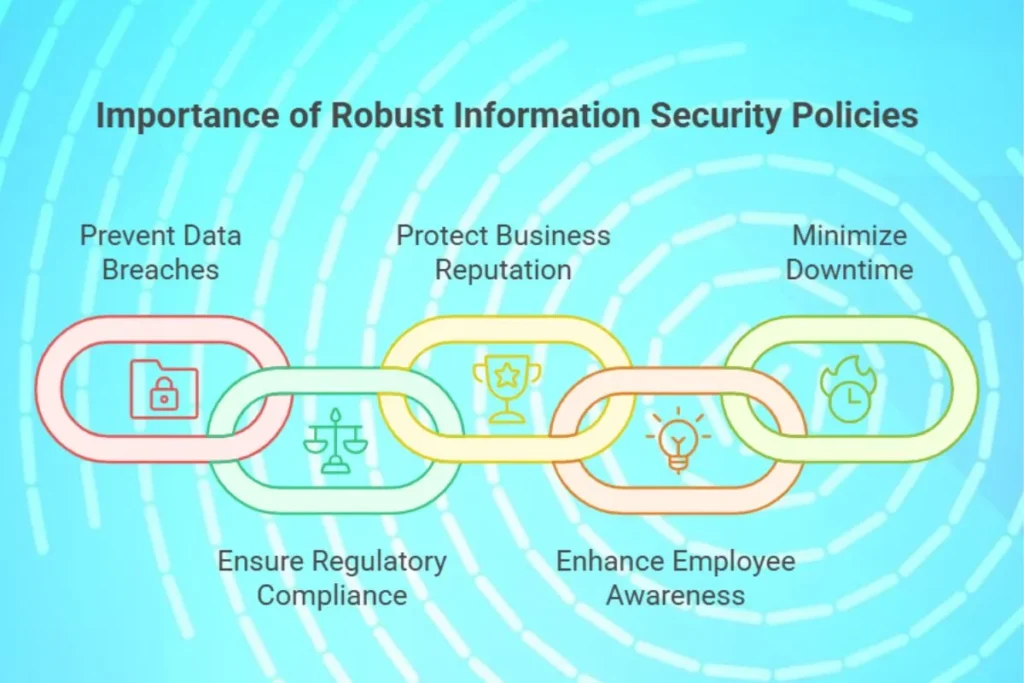
Importance of Information Security Policies
An information security policy is a documented set of rules, procedures, and guidelines that dictate how a business protects its information assets. These policies act as a framework for managing risks and ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Prevent Data Breaches: Establishing clear protocols reduces the likelihood of security incidents.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, are required to adhere to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
- Protect Business Reputation: A robust security policy demonstrates to customers and stakeholders that the business takes data protection seriously.
- Enhance Employee Awareness: Policies educate employees about their roles and responsibilities in maintaining information security.
- Minimize Downtime: Clear guidelines help businesses quickly address and recover from security incidents, reducing downtime.
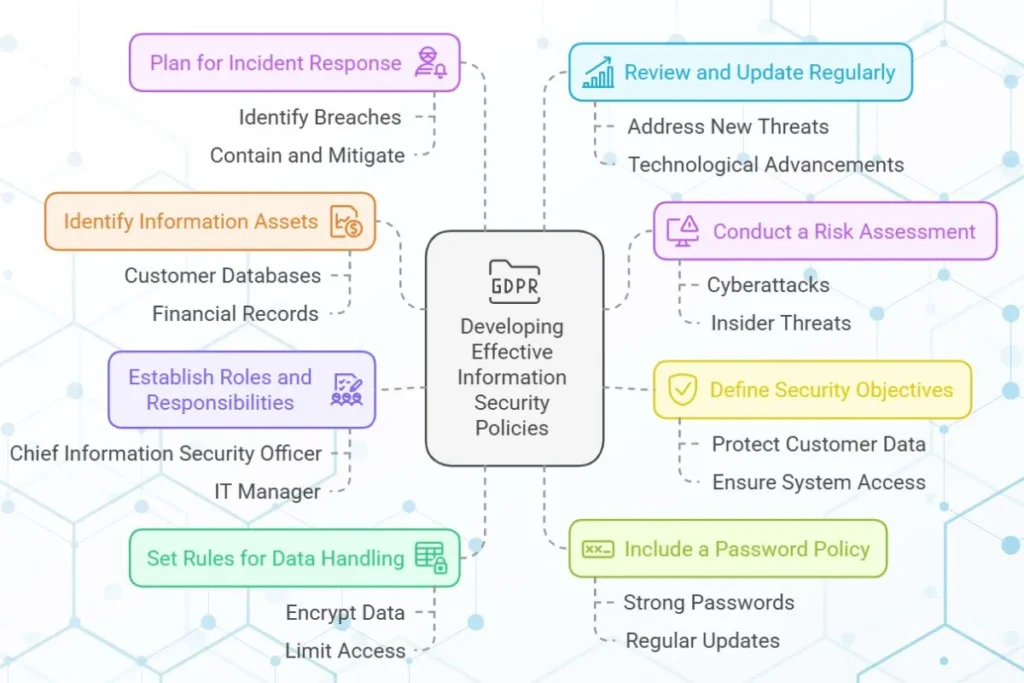
Developing Effective Information Security Policies
Here are the key steps businesses should follow to create effective information security policies:
1. Identify Information Assets
Begin by identifying all the information assets your business handles. These may include customer databases, financial records, intellectual property, and employee information. Consider both digital and physical assets to ensure comprehensive protection.
2. Conduct a Risk Assessment
Assess potential risks to your information assets. This involves identifying threats (e.g., cyberattacks, insider threats) and vulnerabilities (e.g., outdated software, weak passwords). A thorough risk assessment helps prioritize security measures based on potential impact.
3. Define Security Objectives
Clearly outline the objectives of your security policies. For example, “Protect customer data from unauthorized access” or “Ensure uninterrupted access to critical business systems.” Setting measurable goals ensures that progress can be tracked effectively.
4. Establish Roles and Responsibilities
Assign roles and responsibilities for implementing and maintaining security measures. For instance, designate a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or IT manager to oversee security initiatives. Define clear accountability for each team member to avoid confusion.
5. Set Rules for Data Handling
Define rules for handling sensitive data, including storage, transmission and disposal. For example:
- Encrypt sensitive data before sharing it over email.
- Shred physical documents containing confidential information.
- Limit access to sensitive files based on job requirements.
6. Include a Password Policy
Enforce rules for creating strong passwords, such as requiring a mix of letters, numbers and symbols. Encourage employees to update passwords regularly. Use password managers to simplify password management and enhance security.
7. Plan for Incident Response
Outline a detailed incident response plan that includes steps for identifying, containing and mitigating security breaches. Regularly test the plan through simulated exercises to ensure its effectiveness.
8. Review and Update Regularly
Security policies should be reviewed and updated periodically to address new threats and technological advancements. Regular updates ensure that your policies remain relevant and effective.
Real-World Examples of Information Security Breaches
- Equifax Data Breach (2017)
Personal information of over 147 million people was exposed due to unpatched software vulnerabilities.
Lesson Learned: Regularly update software and patch vulnerabilities promptly. - Target Data Breach (2013)
Hackers gained access to Target’s payment system through a third-party vendor.
Lesson Learned: Implement strict security protocols for third-party vendors and monitor vendor activities closely. - Yahoo Data Breaches (2013-2014)
Over 3 billion accounts were compromised due to inadequate encryption practices.
Lesson Learned: Use strong encryption methods to protect sensitive data and conduct regular security reviews. - Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack (2021)
A ransomware attack disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S. East Coast.
Lesson Learned: Invest in robust backup systems and network monitoring to detect and respond to attacks swiftly.
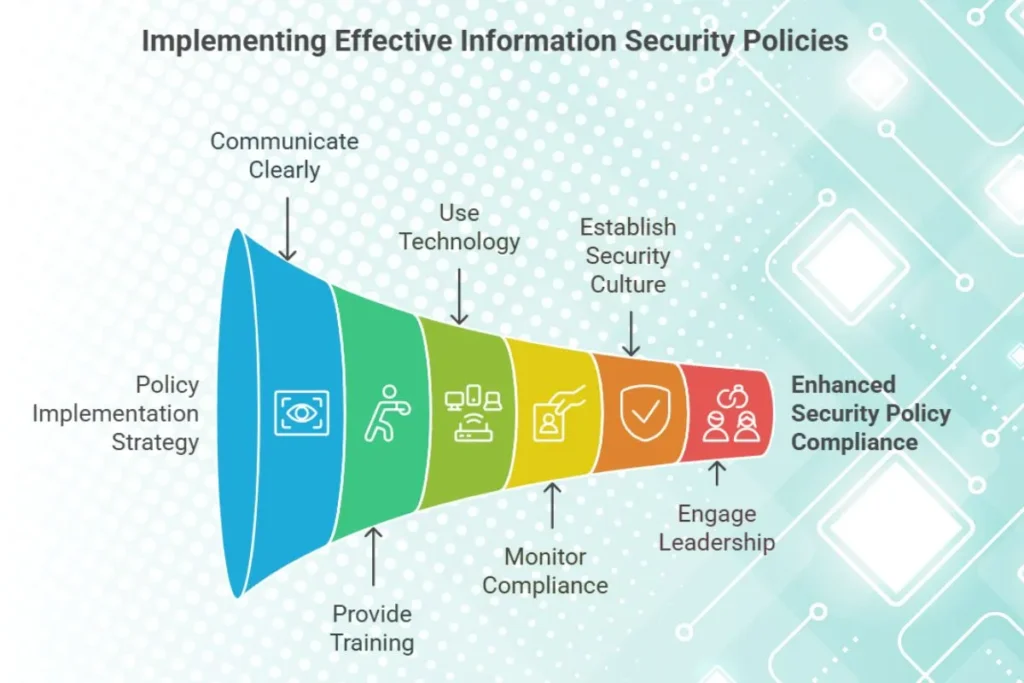
Tips for Implementing Information Security Policies
- Communicate Clearly: Ensure that employees understand the policies and their importance.
- Provide Training: Conduct regular training sessions to keep employees informed about security best practices.
- Use Technology: Use tools like firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems to enhance security.
- Monitor Compliance: Regularly audit compliance with security policies and address any gaps.
- Establish a Culture of Security: Encourage employees to prioritize security in their daily tasks and reward proactive behavior.
- Engage Leadership: Secure commitment from senior management to allocate resources and drive security initiatives effectively.
Conclusion
Information security in business is a very important and fundamental function that protects your assets, reputation and customer trust. By implementing well defined information security policies, businesses can minimize risks, ensure compliance and safeguard their operations.
Hence identify your information assets, assessing risks and create a comprehensive security policy suitable to your organization’s needs. Regular reviews and updates ensure that policies remain effective while combating emerging threats.
Remember, a proactive approach to information security is the key to stay ahead of potential threats and build a secure future for your business. With the right policies in place, businesses can confidently navigate the digital world by protecting their most valuable assets.

