E-commerce websites handle sensitive customer data every day, including personal information and payment details. As online shopping grows, so at the same time cyber threats also grow. You need to ensure strong cybersecurity practices for your e-commerce site to protect your customers, maintain trust and keep your business secure.
In this blog post, we will discuss about the top cybersecurity practices for E-commerce websites, how to ensure E-commerce website safety and provide real world examples with actionable tips.
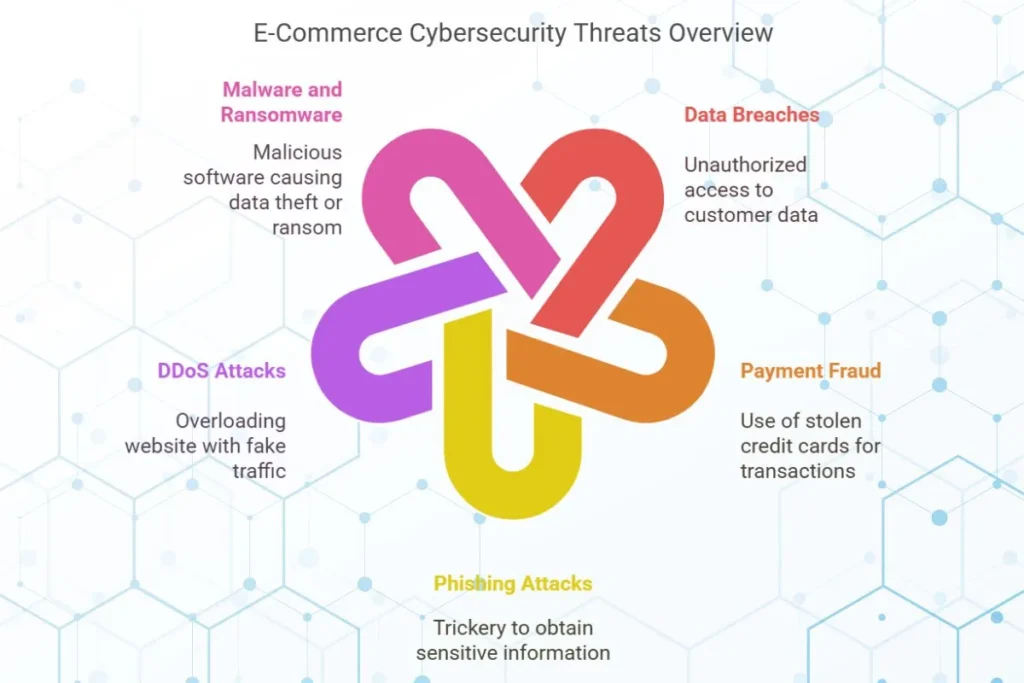
Common Cybersecurity Threats Faced by E-Commerce Websites
Before diving into solutions, let’s understand the threats your e-commerce business might face:
Data Breaches
-
- Unauthorized access to customer data, such as names, addresses and credit card details.
- Example: In 2018, the British Airways data breach compromised the personal and financial details of 380,000 customers.
Payment Fraud
-
- Use of stolen credit cards or fraudulent transactions.
- Example: Fake orders placed using stolen credit card details can lead to financial losses and chargebacks.
Phishing Attacks
-
- Cybercriminals trick customers or employees into sharing sensitive information through fake emails or websites.
DDoS Attacks
-
- Overloading your website with fake traffic, causing downtime and lost sales.
Malware and Ransomware
-
- Malicious software can steal data or lock your systems until a ransom is paid.
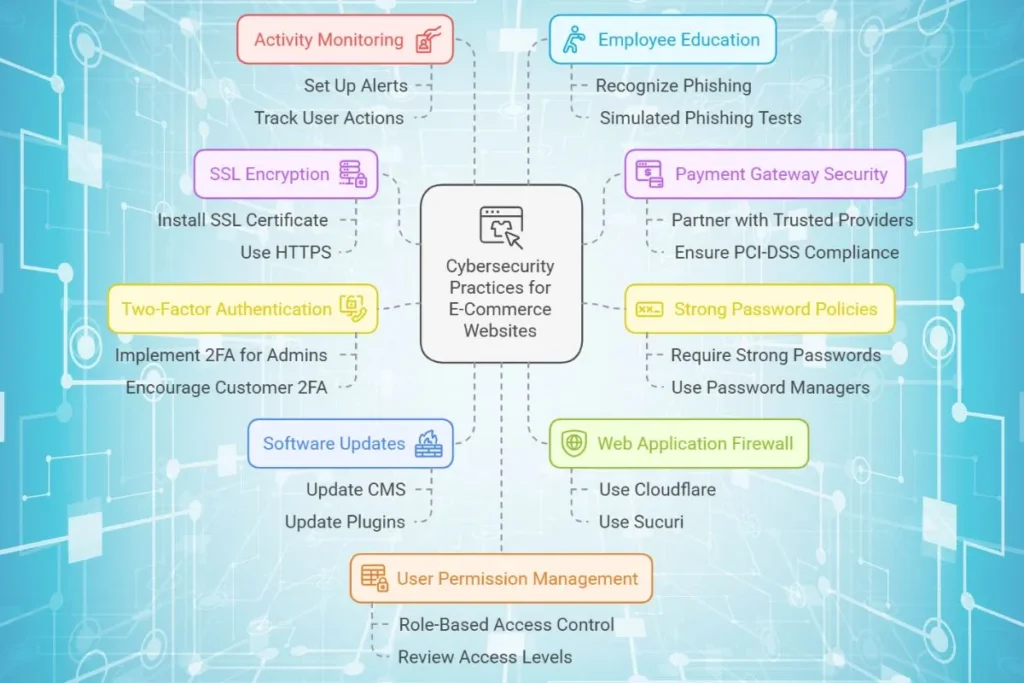
Top Cybersecurity Practices for E-Commerce Websites
1. Use SSL Encryption (HTTPS)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encrypts data exchanged between your website and users. This prevents hackers from intercepting sensitive information like login credentials and payment details. Install an SSL certificate and ensure your site uses HTTPS. Most web hosting providers offer free SSL certificates. HTTPS websites show a padlock icon in the browser, reassuring customers their data is safe.
2. Secure Your Payment Gateway
A secure payment gateway ensures customer transactions are encrypted and processed safely. Partner with trusted payment providers like PayPal, Stripe, or Razorpay. Ensure your payment gateway is PCI-DSS compliant to meet industry security standards.
3. Enforce Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are an easy entry point for hackers. Require users to create strong passwords with a mix of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Use a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords. Instead of “123456,” a strong password might be “G8#pQz4@9.”
4. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to verify their identity with a second factor, such as a code sent to their phone. Implement 2FA for admin accounts and encourage customers to use it. Popular options include Google Authenticator or SMS-based verification.
5. Regularly Update Software and Plugins
Outdated software often has vulnerabilities that hackers exploit. Regularly update your website’s CMS, plugins, and themes. Enable automatic updates when possible. Platforms like WordPress release frequent security patches to address vulnerabilities.
6. Set Up a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF protects your website from malicious traffic by filtering out harmful requests. Use tools like Cloudflare or Sucuri to monitor and block suspicious activity. A WAF can also help prevent DDoS attacks.
7. Monitor and Log Website Activity
Regular monitoring helps to detect suspicious behavior early. Use activity logs to track user and admin actions on your site. Set up alerts for unusual login attempts or large data downloads.
8. Educate Employees on Cybersecurity
Human error is one of the leading causes of data breaches. Train employees to recognize phishing attempts and practice safe online habits. Conduct simulated phishing tests to improve awareness.
9. Restrict User Permissions
Limit access to sensitive data and functions based on user roles. Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to assign permissions only to those who need them. Regularly review user access levels and revoke permissions for inactive accounts.
10. Backup Your Data
Regular backups ensure you can recover your website and data in case of a cyberattack. Schedule automatic backups of your website and store them securely. Keep backups in multiple locations, such as cloud storage and offline drives. Use backup tools like UpdraftPlus or CodeGuard.
11. Perform Regular Security Audits
Security audits help identify vulnerabilities and gaps in your defenses. Use tools like Qualys or Nessus to scan for vulnerabilities. Hire ethical hackers to perform penetration tests.
Real-World Examples of E-Commerce Security Breaches
- Adobe (2013)
- 38 million user accounts were compromised due to a data breach.
- Lesson: Encrypt sensitive customer data and use strong password hashing algorithms.
- eBay (2014)
- Attackers accessed the data of 145 million users by stealing employee login credentials.
- Lesson: Enforce strong password policies and implement 2FA for admin accounts.
- Target (2013)
- A malware attack on Target’s payment system affected 40 million customers.
- Lesson: Regularly update software and monitor for unusual activity.
Building Customer Trust Through Cybersecurity
Customers are more likely to shop from secure websites. Here are ways to build trust:
- Display Trust Badges: Add security badges like Norton Secured, McAfee Secure or PCI-DSS compliance logos.
- Create a Privacy Policy: Clearly explain how customer data is collected, used, and protected.
- Use Secure Payment Options: Offer reputable payment gateways to reassure customers their financial information is safe.
- Provide Transparency: Notify customers promptly in case of a security issue and explain the steps being taken.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is very important for the success and reputation of your e-commerce business. By following these practices, you can protect your website from cyber threats and ensure a safe shopping experience for your customers.
Remember, cybersecurity is not a one time task, but it requires continuous effort and alertness. Take action today to secure your e-commerce website and build trust with your customers; as it is essential for survival in this digital age.

