Now a days ‘Data Analytics’ has become a important tool for businesses across industries. It is a process that allows organizations to transform raw data into actionable tips, which helps them to take smarter and faster decisions based on analyzed data.
In this guide, we shall explore what is data analytics; along with its different types and why it is important for businesses to use this powerful tool.
What is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics is the science of examining raw data to identify patterns, trends and information. Through various techniques, data analytics turns large sets of data into valuable information. This information is used to take decisions in marketing, sales, product development, customer service and many more.
Data analytics involves collecting, processing and analyzing data to reveal trends and patterns. It allows businesses to answer important questions, like:
– How are customer preferences changing over time?
– What factors lead to increased sales or customer churn?
– Which areas of operation can be optimized for efficiency?
Key Types of Data Analytics
To better understand data analytics, it is essential to look at the four main types, each type serves a unique purpose in the decision making process:
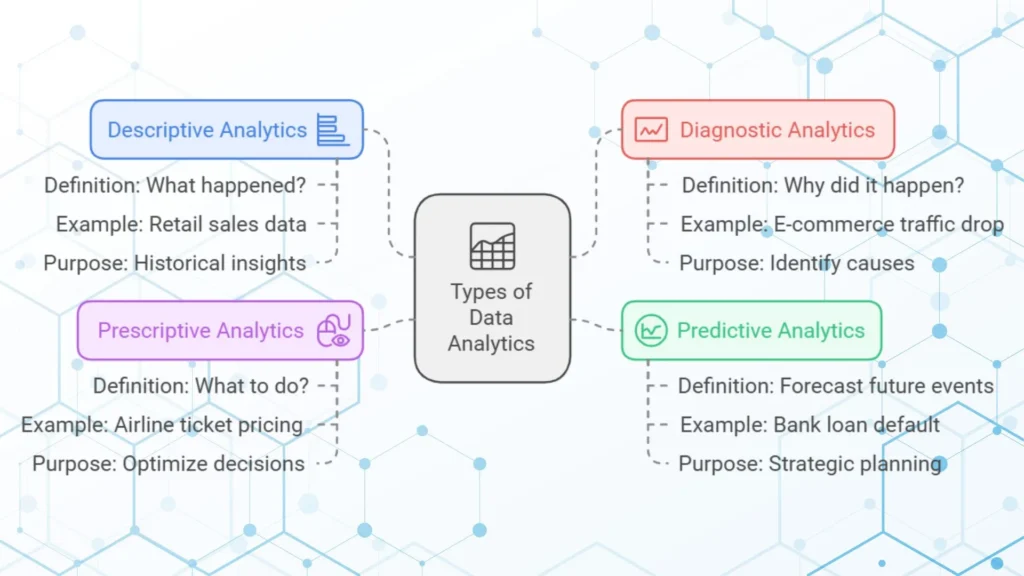
1. Descriptive Analytics
– Definition: Descriptive analytics looks at past data to answer, “What happened?”
– Example: A retail company analyzes sales data from the previous quarter to understand seasonal trends.
– Purpose: It helps businesses to get information about historical performance, which provides a foundation for further analysis.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
– Definition: Diagnostic analytics digs deeper into data to understand “why” something happened.
– Example: An e-commerce company might investigate a sudden drop in website traffic by analyzing referral sources, user engagement and potential technical issues.
– Purpose: This analysis helps businesses to pinpoint the causes of specific outcomes or events, which enables them to solve issues and prevent them to occur in the future.
3. Predictive Analytics
– Definition: Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning models to forecast future events or trends.
– Example: A bank uses predictive analytics to assess the likelihood of loan default based on a customer’s credit history, income and other data points.
– Purpose: By predicting future trends, businesses can plan strategically and prepare for possible scenarios to prevent loss.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
– Definition: Prescriptive analytics suggests actions based on data tips, which helps businesses decide “what to do” to achieve desired results.
– Example: An airline uses prescriptive analytics to set dynamic ticket prices, adjusting for demand, booking patterns and competitor pricing.
– Purpose: It provides specific recommendations, often powered by AI, to optimize decision making and achieve goals effectively.
Importance of Data Analytics
Data analytics enables businesses to make informed decisions, optimize processes and stay competitive. Here are some key reasons why data analytics is essential in today’s business environment:
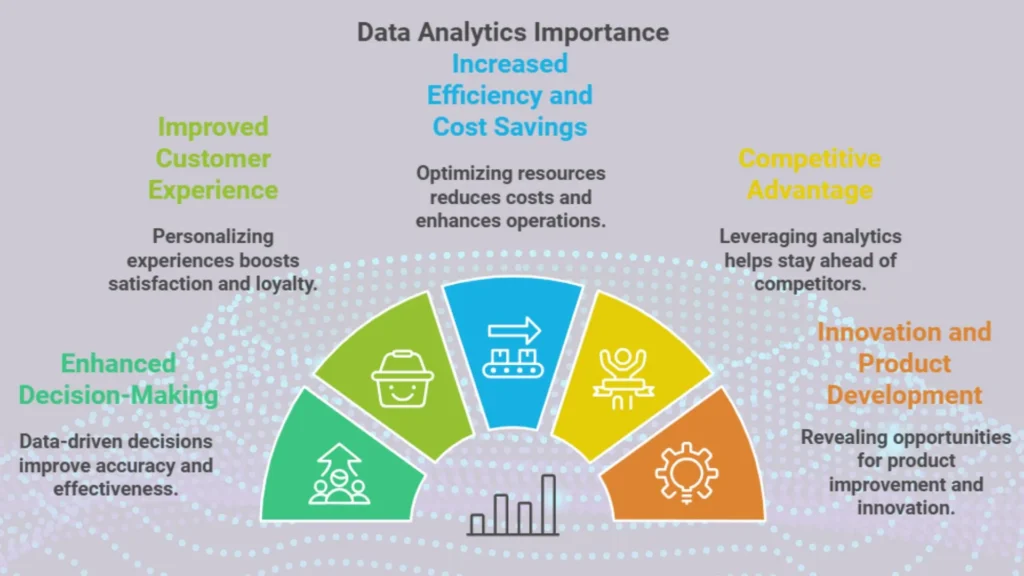
1. Enhanced Decision Making
– Explanation: Data driven decisions are more accurate than those based on intuition alone.
– Example: Starbucks uses data analytics to determine store locations, inventory needs and marketing strategies, which ensures that they meet customer demands effectively.
2. Improved Customer Experience
– Explanation: By analyzing customer behavior and preferences, businesses can personalize experiences, which boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty.
– Example: Netflix uses data analytics to suggest content to viewers, matching recommendations based on individual viewing habits.
3. Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings
– Explanation: Analytics can discover inefficiencies in operations, which enables businesses to optimize resources and reduce costs.
– Example: General Electric (GE) uses data analytics in predictive maintenance, by monitoring equipment performance and thus reduces downtime in manufacturing plants.
4. Competitive Advantage
– Explanation: Businesses that effectively use data analytics are better positioned to stay ahead of competitors, who respond more quickly to market changes.
– Example: Amazon uses predictive analytics to optimize its supply chain and inventory management, which enables faster delivery times and higher customer satisfaction.
5. Innovation and Product Development
– Explanation: Data analytics can reveal new opportunities for product improvement or innovation, which allows businesses to meet evolving customer needs.
– Example: Procter & Gamble (P&G) uses data analytics to understand customer preferences and adjust product lines, such as developing eco friendly packaging based on consumer tips.
Real World Case Studies
1. Walmart and Inventory Management
– Walmart uses data analytics to optimize inventory, which ensures the right products are stocked based on demand. By analyzing data from sales, weather patterns and local events, Walmart ensures it can meet customer demand efficiently. This approach saves costs and also improves customer satisfaction.
2. Airbnb’s Price Prediction Model
– Airbnb uses predictive analytics to help the hosts to set optimal prices based on demand, seasonality and local events. This data driven approach benefits the hosts by maximizing their earnings while ensuring competitive pricing for guests.
3. UPS and Route Optimization
– UPS uses prescriptive analytics to determine the most efficient delivery routes, which saves fuel and reduces delivery times. By analyzing data from millions of deliveries, UPS can optimize its operations, cut down costs and improve customer service.
How to Implement Data Analytics in Your Business
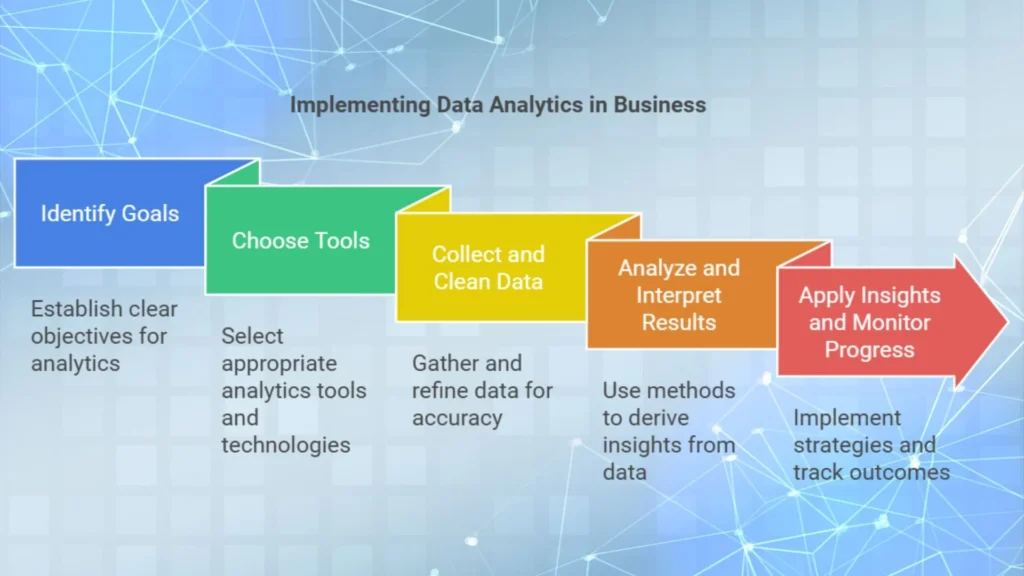
1. Identify Your Goals
– Before starting with data analytics, establish clear goals, such as improving customer satisfaction, increasing revenue, or reducing costs etc.
2. Choose the Right Tools and Technologies
– Choose popular data analytics tools like Google Analytics, Tableau, Power BI and specialized machine learning platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure.
3. Collect and Clean Data
– High quality and accurate data is essential. Invest time in cleaning data to remove duplicates and inaccuracies, to ensure reliable analysis.
4. Analyze and Interpret Results
– Use statistical methods and visualization tools to interpret the data, to transform numbers into actionable tips.
5. Apply tips and Monitor Progress
– Implement data driven strategies, monitor the results and refine your approach based on feedback and new data.
Conclusion
Data analytics is a necessity for businesses that want to make progress in todays modern world. As data continues to grow in volume and value, mastering data analytics will remain essential for businesses to stay competitive, innovative and meet the customer expectations.
By understanding its types and benefits, businesses can utilize the power of data to improve decision making, boost efficiency and deliver superior customer experiences. Incorporate data analytics into your operations to add significant value and ensure long term success for your business.

