In recent years, computer vision technology has become one of the most innovative fields within artificial intelligence. By enabling machines to ‘see’ and interpret visual data, computer vision has changed industries like healthcare, retail business, manufacturing etc. As technology advances, the applications of computer vision are expanding rapidly, which enhances efficiency, accuracy and innovation across various fields.
In this article, we shall discuss how computer vision technology works, also we shall explore its main concepts, look at its applications in different industries and discuss the challenges and advancements that shapes its future.
What is Computer Vision
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that trains computers to translate and make decisions based on visual data, such as images and videos. By duplicating the human visual system, computer vision allows machines to recognize objects, detect patterns and extract information from visual inputs. This technology plays a important role to enable applications like facial recognition, autonomous driving and quality inspection in manufacturing industries.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision relies on several techniques and models to process and analyze images:
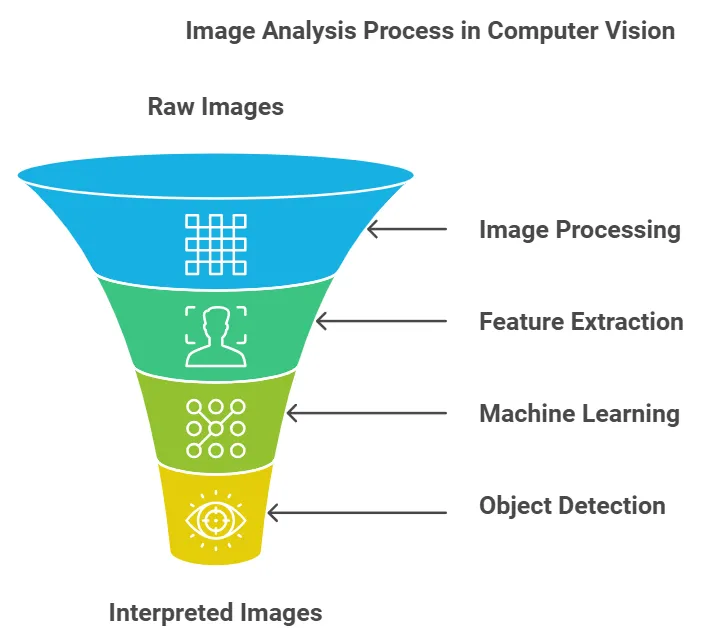
1. Image Processing: Preprocessing steps like resizing, filtering and normalization prepare images for analysis.
2. Feature Extraction: Key features like edges, colors and textures are extracted from images to make them easier for algorithms to analyze.
3. Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Machine learning models and deep neural networks help to recognize patterns and classify objects in images.
4. Object Detection and Recognition: Advanced algorithms identify and label objects within an image, which enables computers to translate complex scenes.
Key Concepts in Computer Vision
Computer vision consists of many major concepts that enable machines to analyze visual data effectively. Here are a few of the most important ones:
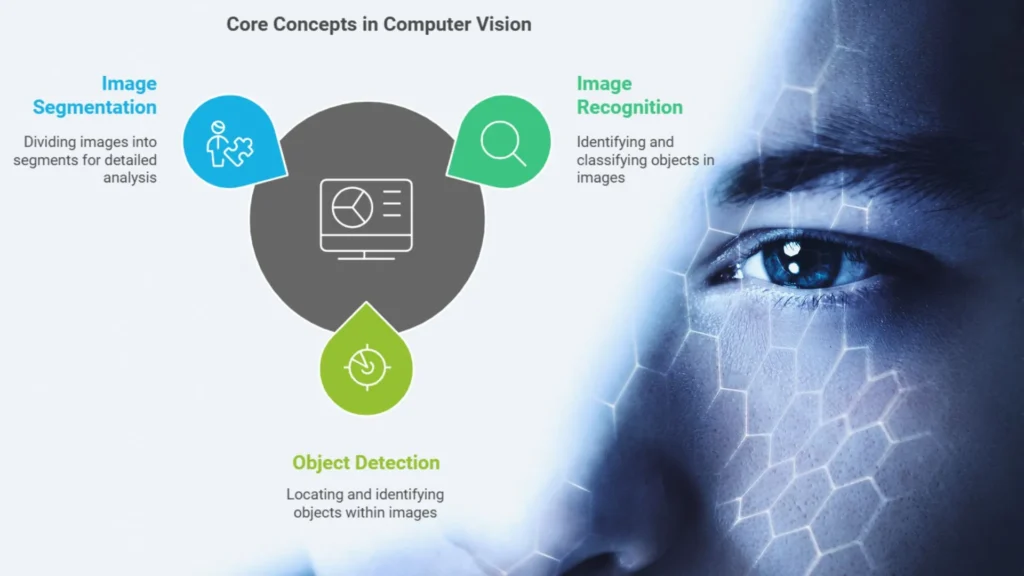
1. Image Recognition
What It Is: Image recognition is the process of identifying and classifying objects within an image. For example, a computer vision model can recognize a cat in a photo by analyzing features like shape, texture and color.
Applications:
– Social Media: Platforms like Facebook use image recognition to detect faces in photos and suggest tags.
– E-commerce: Image recognition is used in visual search tools, which enables customers to search for products using images instead of text.
2. Object Detection
What It Is: Object detection goes beyond simple recognition by identifying objects and also locating them within an image. This is necessary for applications where understanding the position of objects is important, such as autonomous driving.
Facial recognition is a subset of object detection specifically focused on identifying and verifying individual faces within an image. This technology has gained popularity in security, to allow secure authentication in devices and access systems.
Applications:
– Autonomous Vehicles: Object detection is used to identify pedestrians, vehicles and obstacles on the road.
– Retail Analytics: In retail business, object detection can help to analyze customer behavior by tracking products picked up or returned to shelves.
3. Image Segmentation
What It Is: Image segmentation divides an image into multiple parts or segments, typically by distinguishing objects from the background. This is important in scenarios where precise object boundaries are needed.
Applications:
– Medical Imaging: Segmentation is used to identify and isolate areas of interest, such as tumors in MRI scans.
– Agriculture: Image segmentation helps monitor crop health by isolating plants from the soil background.
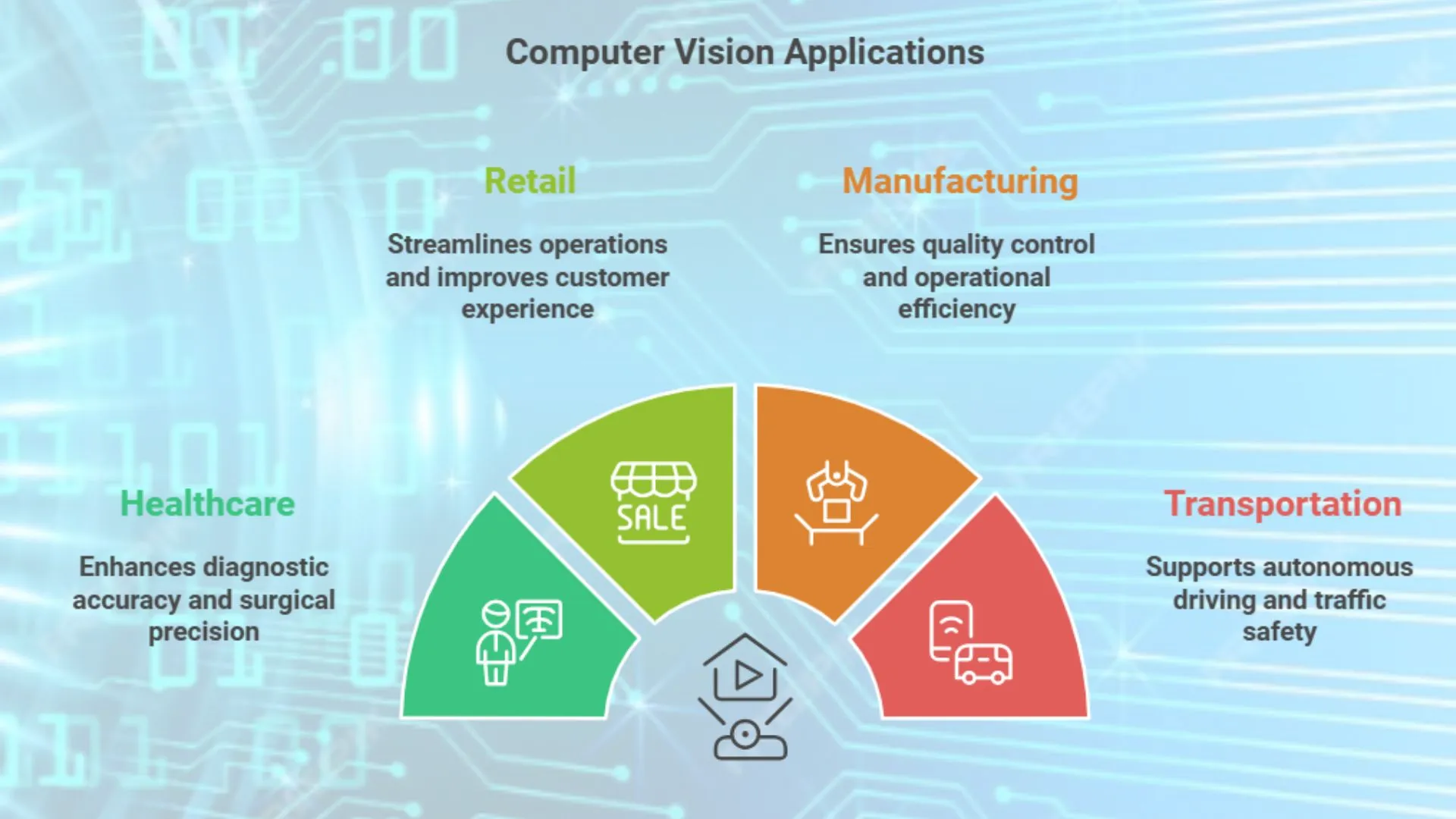
Applications of Computer Vision in Various Industries
Computer vision is making a significant impact across a many industries. Let us explore some noteworthy use cases.
1. Healthcare
Computer vision is transforming healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and reducing the burden on medical professionals. Here are a few applications:
– Medical Imaging: Computer vision models can analyze X-rays, MRIs and CT scans to detect abnormalities such as tumors, fractures and infections. For instance, AI algorithms can assist radiologists by highlighting suspicious areas, to enable faster and more accurate diagnosis.
– Surgical Assistance: In robotic assisted surgeries, computer vision guides robotic arms, to improve precision and reduce risks.
– Patient Monitoring: Computer vision systems monitor patient movement to alert staff to potential falls or injuries.
Case Study: Researchers at Stanford developed an AI model capable of diagnosing pneumonia from chest X-rays with accuracy comparable to experienced radiologists. This advancement demonstrates the potential of computer vision to support healthcare professionals in critical diagnoses.
2. Retail
Computer vision is changing the retail sector by enhancing customer experience and streamlining operations. Here are some popular applications:
– Automated Checkout: Stores like Amazon Go use computer vision to track items customers pick up, to enable a seamless, checkout free shopping experience.
– Inventory Management: Cameras and computer vision algorithms monitor stock levels in real time, to alert staff when shelves need restocking.
– Customer Insights: Computer vision systems analyze in store video footage to understand customer behavior, which helps retailers to optimize store layout and improve customer engagement.
3. Manufacturing
Computer vision is enhancing quality control and operational efficiency in manufacturing. Here are a few ways it is being applied:
– Quality Inspection: Computer vision systems inspect products on assembly lines, to identify defects or inconsistencies. This ensures that only products that meet quality standards reach to customers.
– Predictive Maintenance: Cameras and computer vision detect wear and tear in equipment, which predicts potential failures and prevents costly downtime.
– Robotics: In smart factories, robots use computer vision to navigate environments and handle materials with precision.
Case Study: BMW uses computer vision systems in its factories to identify and correct defects in car parts. This helps the company maintain high quality standards and reduce waste from defective products.

4. Transportation
Computer vision plays a important role in the development of autonomous vehicles and to improve transportation safety.
Use Cases:
– Autonomous Driving: Self driving cars rely on computer vision to detect pedestrians, obstacles, traffic lights and road signs. Companies like Tesla and Waymo use Computer Vision based object detection and image segmentation for safe navigation.
– Traffic Monitoring: CV systems monitor traffic patterns, detect violations and optimize traffic flow to reduce congestion.
Challenges in Computer Vision
Despite its many applications, computer vision still faces several difficulties that researchers and engineers are working to overcome.
1. Data Quality and Variability
Computer vision models require large volumes of labeled data to train effectively. However, obtaining high quality, diverse datasets can be difficult. Models trained on limited or biased datasets may struggle with real world variations, such as changes in lighting or object orientation.
2. Real Time Processing Power
Many applications, such as autonomous driving, require real time image processing. Achieving this requires powerful hardware and optimized algorithms, as even a minor delay could result in safety risks.
3. Privacy and Ethical Concerns
As computer vision becomes more widespread, privacy concerns are increasing. Surveillance systems powered by computer vision can potentially go against individuals’ privacy if used irresponsibly. As this technology continues to grow, it is essential to ensure ethical use and respect data privacy.
4. Adversarial Attacks
Computer vision models can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where tiny modifications to input images deceive the model into making incorrect predictions. This situation is dangerous, especially in safety related applications like security and autonomous vehicles.
Advancements in Computer Vision
Recent developments are pushing the boundaries of computer vision. Some of the most promising developments include:
1. Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Deep learning, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), has greatly improved image recognition accuracy. CNNs are designed to process visual data, to make them highly effective for computer vision tasks. This technology is behind many modern applications, from facial recognition to real time video analysis.
2. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning allows models to use pre trained networks, which reduces the amount of data and computing power required for new tasks. For example, pre trained models like ResNet and VGG can be fine tuned to perform specific computer vision tasks, to speed up deployment in real-world applications.
3. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) consist of two models that compete against each other to improve output quality. GANs are used in image generation, enhancement and style transfer. They are also applied in fields like fashion and entertainment to generate realistic images and videos.
4. Edge Computing
Edge computing enables computer vision to process data closer to the source, which reduces latency and reliance on cloud infrastructure. This advancement is especially valuable in applications like autonomous driving, where real time processing is very important for safety.
Conclusion
Computer vision technology is changing industries by enabling machines to interpret and respond to visual data. Industries like healthcare, retail, manufacturing and transportation taking advantage of computer vision applications for improving efficiency, accuracy and decision making. However, this technology also faces challenges, such as data quality, real time processing requirements and privacy concerns.
As technology continues to evolve, computer vision will play an increasingly important role as how we interact with machines and use data to solve complex problems.
By understanding the capabilities, limitations and ethical considerations of computer vision, businesses and developers can use this technology to create impressive and innovative solutions to benefit society.

