Facial recognition technology has become a major part of modern security, which enables to unlock smartphones and even personalized customer experiences in retail business. By using unique facial features, this technology can identify or verify a person from an image or video. But how does facial recognition technology works and what makes it so effective?
In this comprehensive guide, we shall explain how facial recognition technology works, the main components involved in identifying unique facial features, real world applications across various sectors and the privacy and ethical concerns surrounding its use.
What is Facial Recognition Technology?
Facial recognition is a type of biometric technology that uses algorithms to analyze the unique characteristics of a person’s face. Each person’s facial features, such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the cheekbones and the contour of the lips etc. create a unique ‘facial signature’, much like a fingerprint.
These facial signatures allow facial recognition systems to identify or verify individuals by comparing facial data from a photograph or video to stored images in a database. This process involves complex algorithms, feature extraction and matching techniques to ensure high accuracy.
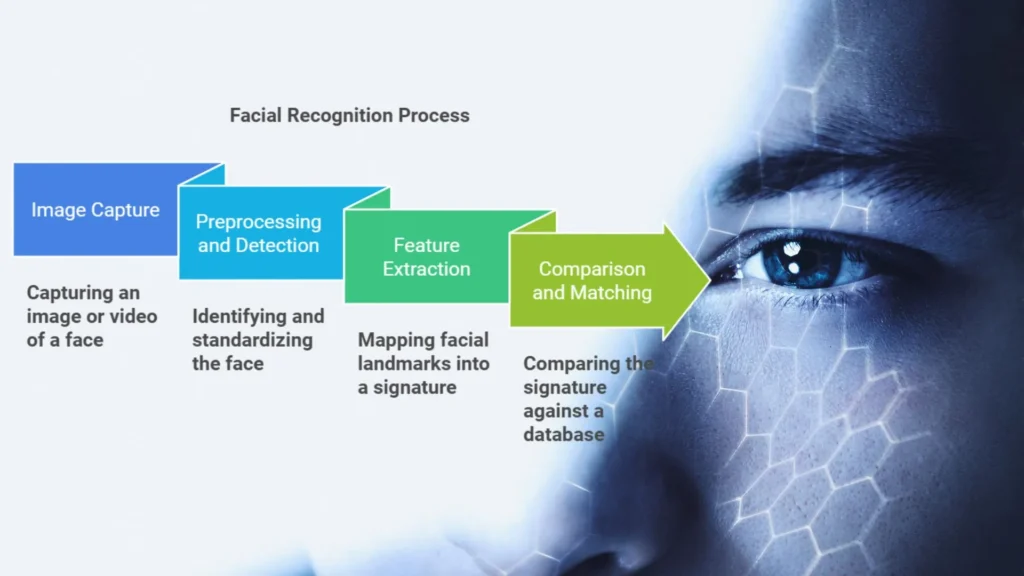
How Facial Recognition Systems Work
1. Image Capture
The process starts with capturing an image or video of a face. This can be done through various devices, such as security cameras, smartphones or computers. The system captures multiple images or frames to ensure it has a clear view of the face from different angles.
2. Preprocessing and Detection
Once the image is captured, the system undergoes a preprocessing stage. Here, algorithms work to identify the face in the image and standardize factors like lighting, angle and resolution. This preprocessing is important for accurate analysis, as it normalizes the image for comparison against others.
3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction is the heart of facial recognition technology. In this stage, the system identifies unique characteristics of the face, called “landmarks.” These can include:
– Distance between the eyes
– Width of the nose
– Depth of the eye sockets
– Shape of the cheekbones
– Contour of the jawline
These ‘landmarks’ are mapped out and converted into a mathematical representation, known as a facial signature. This unique code is what differentiates one person’s face from another.
4. Comparison and Matching
In the final stage, the system compares the extracted facial signature against a database of stored images. There are two main approaches here:
– One-to-One Matching: Also called verification, where the system checks if the face matches a specific image or ID (e.g., unlocking your smartphone with face ID).
– One-to-Many Matching: Also called identification, where the system searches for a match across an entire database (e.g., scanning for a known criminal in a public crowd).
If the system finds a close match based on a similarity score, it identifies or verifies the person. The accuracy depends on the quality of the image, the algorithm used and the database size.
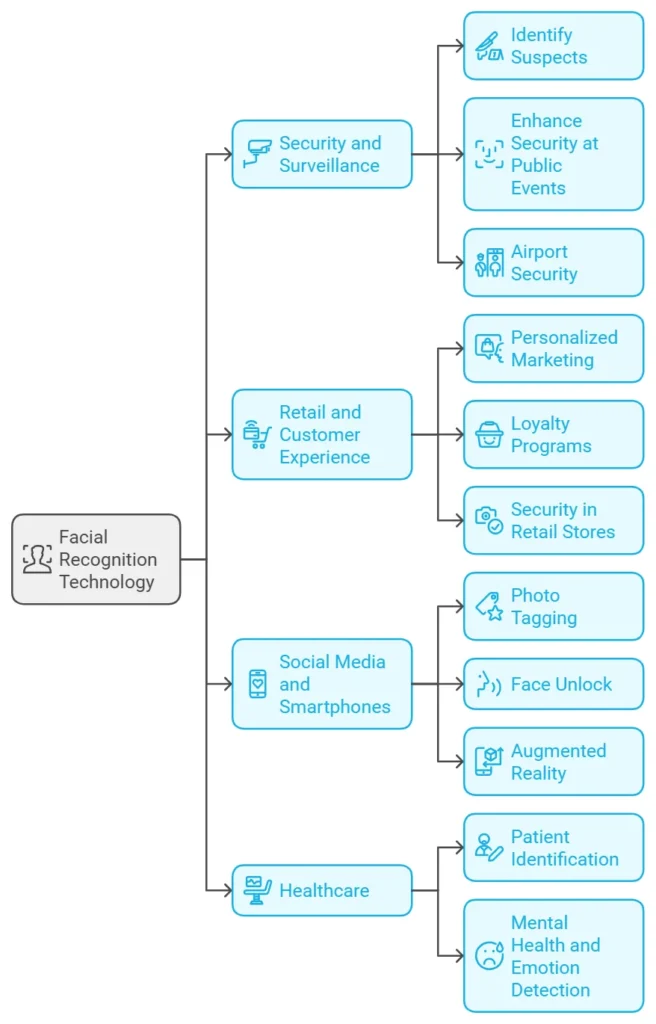
Applications of Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology is widely used across various sectors, each utilizing its power for unique applications.
1. Security and Surveillance
Facial recognition is perhaps most widely recognized for its applications in security and law enforcement. Governments and police departments use it to:
– Identify suspects in criminal investigations: Matching photos or footage from a crime scene with a database of known criminals.
– Enhance security at public events: Monitoring large crowds for individuals on watchlists.
– Airport Security: Many airports have implemented facial recognition for passenger identification, to speed up the boarding process and enhance security.
Case Study: The city of London implemented facial recognition technology across CCTV networks to monitor high traffic areas for security threats. This has helped police to identify individuals with outstanding warrants in real time, to improve public safety.
2. Retail and Customer Experience
In the retail industry, facial recognition technology is used to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Examples include:
– Personalized Marketing: Stores like Sephora are experimenting with facial recognition to identify repeat customers and make suitable shopping experiences based on purchase history.
– Loyalty Programs: Facial recognition can help to recognize loyal customers, so as to offer them special discounts or rewards.
– Security in Retail Stores: To deter shoplifting, some retailers use facial recognition to identify and track known offenders.
Case Study: A grocery store in China uses facial recognition at checkout counters, which allows customers to pay simply by scanning their face. This speeds up transactions and also enhances customer convenience.
3. Social Media and Smartphones
Social media platforms and smartphone companies use facial recognition for both security and convenience:
– Photo Tagging: Platforms like Facebook and Instagram use facial recognition to suggest tags in photos, which makes it easier for users to identify friends and family.
– Face Unlock: Apple’s Face ID and other smartphone brands offer face based unlock mechanisms, which enables users to access their devices securely and easily.
– Augmented Reality (AR): Filters and effects on apps like Snapchat rely on facial recognition to apply fun effects that adjust to users’ facial movements.
4. Healthcare
In healthcare, facial recognition technology has many applications in patient identification, diagnosis and treatment. Some examples include:
– Patient Identification: Hospitals can use facial recognition to verify patient identities, which improves administrative efficiency and prevents medical errors.
– Mental Health and Emotion Detection: Facial recognition algorithms can analyze expressions to detect signs of stress, depression, or anxiety, which helps physicians to diagnose more accurately.
Case Study: Some healthcare providers use facial recognition to monitor patients in critical care. Algorithms can analyze changes in facial expressions to detect signs of pain or distress, which asks for timely medical attention.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Although, facial recognition technology offers many benefits, it also raises many privacy and ethical concerns. Here are some of the key issues:
1. Privacy Invasion
Facial recognition can identify individuals without their consent, especially in public places. This intrusion of privacy is a major concern, as it gives authorities and private companies the ability to monitor people’s movements and behaviors without their knowledge.
2. Bias and Discrimination
Facial recognition algorithms can exhibit bias, particularly if they’re trained on non diverse datasets. Studies have shown that some systems have higher error rates when identifying people of certain ethnicities or genders, which may lead to potential discrimination and inequality.
3. Misuse by Authorities
When used without proper regulation, facial recognition technology can be exploited for surveillance, which limits individual freedom and violate civil rights. Many activists argue that governments should enforce stricter regulations or even ban facial recognition to prevent misuse.
4. Data Security Risks
Facial recognition systems collect and store sensitive biometric data, which, if compromised, can lead to identity theft and other security issues. Protecting this data from hackers and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations is very important.
The Future of Facial Recognition Technology
The future of facial recognition technology looks promising but will depend heavily on advancements and ethical considerations. Here are some trends and areas of focus:
1. Improved Accuracy and Fairness
Researchers are developing techniques to reduce bias and improve accuracy in facial recognition systems. By training models on more diverse datasets, developers can create algorithms that perform fairly across various demographics.
2. Privacy Enhancing Techniques
As privacy concerns rise, new methods are emerging to protect user data. Some facial recognition systems now use techniques like ‘differential privacy‘, where data is anonymized to minimize personal risks.
3. Regulation and Policy
Governments worldwide are beginning to regulate facial recognition technology to treat privacy, ethical and security concerns. For instance, the European Union is considering a temporary ban on facial recognition in public spaces, while several U.S. cities have restricted its use by law enforcement.
4. Multi Factor Authentication
Some companies are combining facial recognition with other forms of identification, such as fingerprint scans or PIN codes, to enhance security. This multi factor authentication approach reduces reliance on facial recognition alone and adds another layer of protection.
5. Integration with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
As AR and VR technology grows, facial recognition could play a role in creating immersive experiences, which allows users to control virtual avatars with facial expressions or engage in more personalized interactions.
Conclusion
Facial recognition technology is a powerful tool that is shaping the future of security, retail business, healthcare and more. By analyzing unique facial features, this technology can identify and verify individuals with impressive accuracy. However, the benefits come with ethical concerns, particularly around privacy and algorithmic bias.
As the field continues to evolve, the focus must remain on balancing innovation with responsible use. With proper regulations and technological advancements to ensure fairness and privacy, facial recognition has the potential to bring significant benefits to society.


Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks.